Installation of a pipeline is a rather complicated matter, although at first glance everything is very clear. Especially when it comes to large-scale works. The point is that not always technical conditions allow digging trenches for laying, but at the same time, not all communications for technical reasons are capable of going above the ground, for example, on struts.
In a number of such cases, the trenchless method of laying pipes is also applicable.
What it is?
Trenchless laying pipes is a set of measures for the creation of a communications wire, in which the method of digging a trench is replaced by a number of other works, and the preliminary deepening itself is not performed.
This method is applicable for the following communications:
As for the materials of the pipes themselves, it does not play a special role for the use of one of the alternative methods. Therefore, a trenchless lining can be made of both metal and polymer products, only taking into account the characteristics of the material and its compounds.
There are several of the most popular trenchless methods.
Horizontal directional drilling
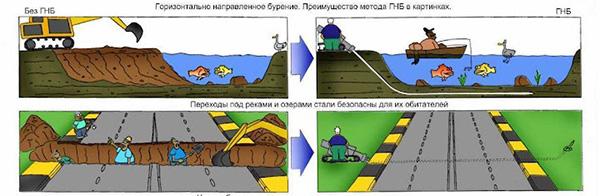
One of the most common options. In this case, a special drilling rig is used for installation. Its popularity lies in its relative reduction in time and effort. In particular, this method is perfectly applicable in difficult ground conditions, for example, in the presence of quicksands, lakes, ravines. Or in the presence of other elements of urban planning: squares, parks, roads, etc. This method is used without opening the surface layer of the earth, which does not spoil the overall landscape. This method is validated and approved.
Punching steel cases
So, the method consists of the following manipulations. Into the ground with the help of special devices, hydraulic jacks, the metal (steel) case is pressed in. One end of the pipe is equipped with a knife. This procedure facilitates the process of entering the land and reduces damage to the surrounding area. After the start of work, the soil enters the pipe due to the high pressure and its hollow space. Then he is taken out of the face. In total, three stages of punching can be distinguished.
- Development of a pit, the width of which should not be less than 3.5 meters, and the length - 4 meters. It must be reinforced, have a depth of half a meter below the pipe chute.
- Preparing the wall for jacks. In this case, a special solution is poured, forming a wall, which will be an emphasis for the equipment.
- The installation of the power equipment is already in the pit. The hydraulic equipment itself can consist of several cylinders (from 1 to 4). The force of the jacks, depending on the soil, ranges from 100 to 500 tons.
Microtunnelling
This collector construction method is well suited for urban environments where areas are limited. For this method, special equipment is used - a tunneling microshield, which translational movements provides a powerful jacking station that transmits the pushing force through the column of reinforced concrete pipes to the shield.
For this, special drilling rigs are used. Drilling takes place without leaving the working pit to the surface into the receiving pit. And a special puncher lays pipes of large diameter, more often from 400 to 1200 mm. The drilling process takes place in several stages.
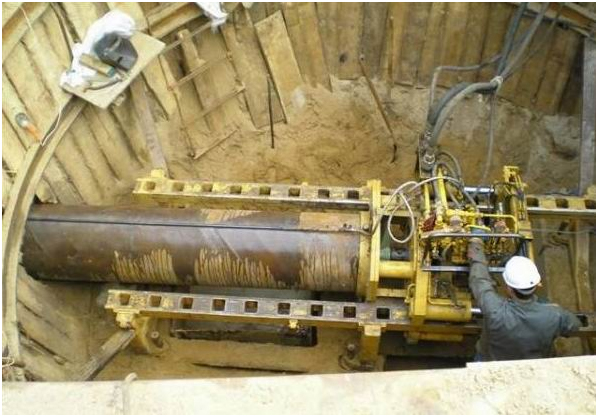

Punctured road
This method is applicable for most types of communication. Moreover, it can be used both in basements of houses and in existing wells.

Features of trenchless pipe laying:
- Reduced deadlines for the execution of even the largest works.
- Increasing the temporary seasonal gap. Thanks to the installations, pipe installation can be carried out in cold weather.
- Reducing costs.
- Minimal red tape associated with the approval of work and obtaining the necessary documentation.
- Compactness. Possible work even on tiny urban areas.
New technologies are very quickly being introduced into modern industries. Thus, it is possible that the trenchless method of laying communications will soon completely replace the classic one with large-scale digging of trenches and immersion of pipes in them.
The centuries-old experience in the construction of structures for various purposes and the communications connecting them has given rise to a lot of ways to implement many projects, including trenchless laying.
It includes trenchless laying methods and various options for its implementation.
There are not many basic options, but taking into account all possible industries of their application, the amount of materials used and the differences in soil media in which they are used, the list expands indefinitely.
The main ones deserve attention, there are 4 of them:
- Horizontal directional drilling.
- Sanitation.
- Puncture.
- Punching.
The first one is considered in a separate article with the same name, so it makes no sense to dwell on it in detail. It should only be noted that it is versatile and most effective in most soils and laying conditions. And the length of the resulting path is measured in hundreds of meters.
Trenchless laying methods
The trenchless method of laying, called remediation, combines a number of different methodologies that allow you to draw a new line by updating an old one. At the same time, depending on what will be done with the old line, 2 groups of methods are distinguished:
- Relining.
- Renovation.
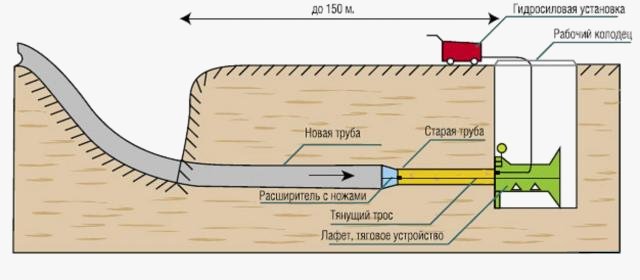
The first option involves keeping the old line. It is cleaned of foreign objects and all kinds of obstacles manually or using various techniques. And then a new line of smaller diameter is laid inside it from new materials that have a longer service life and improved characteristics.
Relining involves a lot of implementation options. Trenchless laying of communications can be carried out in this case both by pulling in pipes from the opposite end of the track, and by pushing them from the starting point of construction (repair). At the initial stage, it is required to disconnect the repaired section from the water supply or sewerage system, with a parallel change in the flow route through temporary pipes. New pipes can be introduced directly from the starting point or at any other point of the pipeline being repaired with its partial destruction for the introduction of a new pipe. At the end of the installation, the flow is reconnected from the temporary pipes to the permanent renewed paths.
The second option - Renovation, implies a complete renewal of the line with a possible decrease or increase in the diameter of the flow due to the static destruction of the previous structure. At the same time, its fragments are not brought to the surface, but remain inside, creating a compacted shell around the new structure.
Refurbishment allows replacing almost all old types of pipes, from ceramic and concrete structures to metal variations.
The next two methods (piercing and punching) are used to create completely new underground paths. The disadvantage of the puncture method is that the maximum duration of the laying section is only 60 m.This is due to the fact that such a trenchless pipe laying implies significant efforts on the part of equipment from 150 to 3000 kN. It is carried out using hydraulic jacks, winches, tractors and bulldozers. In this case, the puncture is carried out by a directly installed pipe with a tapered tip installed on it with additional knives. The pressure is transferred to it from the pipe, which receives it from the equipment. And under its influence, a path is laid with the creation of a seal around the pipe, which subsequently does not require sprinkling, but only welding during installation.
Punching is performed in the same way, however, without using a nozzle. Thus, there will be no seal around the pipe, and the entire mass of soil obtained by punching will be inside metal pipe... This content is displayed at the final stage of the installation. In this case, the length of the pipe, if used, will not exceed 100 m. This type of construction is most often used as a trenchless sewerage installation.
Trenchless pipeline laying was developed by Western experts. However, due to its high efficiency, this methodology was adopted by domestic firms, which disseminated it, and also created their own devices used in parallel with foreign counterparts.
Of the advantages that distinguish the described technologies, it is worth highlighting:
- Minimal impact of laying season.
- Reducing the degree of human interference.
- Reduction of the used human resources.
- Minimization of the time spent on all operations.
- Preservation of aboveground infrastructural and natural objects.
- Few by-products.
The lack of seasonality in the work allows updating or laying in emergency conditions, when urgent intervention of repair services is required to replace communications.
A minimum of human resources on the construction site improves the safety of the work and therefore reduces the number of permits for renovation or construction operations.
The work time is reduced to 4-40 m / h, depending on the method used, which is practically unattainable in similar open-type operations, not only with the use of a large amount of human resources, but also technology.
The preservation of surface structures is invaluable. So, such means can be used on the territory of objects of historical and cultural value, the destruction of which is unacceptable. In addition, vegetation, fertile soil cover is preserved, and the use in densely populated regions allows not to disrupt traffic flows and the usual rhythm of life of the population. The last argument is the amount of by-products. Compared to open methods, trenchless pipe laying reduces this pollution by several times.
Trenchless Piping Videos
 And in translation it's just "don't dig". After all, how often we laugh at the communal workers about the fact that the road services did not have time to lay the asphalt, as it was blown up to lay the heating main. Another situation: a motorway of republican or international importance began to swamp and flood on one side, you need to put a pipe under it to drain water, but you cannot dig the road - there is no detour. Or: through an old park, where every tree is a monument of history and nature, you need to lead to the farm, which has become a museum, gas and water ... Thanks to new technologies, in particular, trenchless laying of communications, all these tasks are solved quickly and painlessly for nature.
And in translation it's just "don't dig". After all, how often we laugh at the communal workers about the fact that the road services did not have time to lay the asphalt, as it was blown up to lay the heating main. Another situation: a motorway of republican or international importance began to swamp and flood on one side, you need to put a pipe under it to drain water, but you cannot dig the road - there is no detour. Or: through an old park, where every tree is a monument of history and nature, you need to lead to the farm, which has become a museum, gas and water ... Thanks to new technologies, in particular, trenchless laying of communications, all these tasks are solved quickly and painlessly for nature.Methods for trenchless laying of communications
There are at least seven of them, but the choice of a specific method depends on the purpose and depth of the communications to be laid, on their size, on the mechanical composition of the soil, on the length of the hole being made, on the power of the power drive.
The most common are the following:
- - method of horizontal mechanical drilling;
- - method of puncture and punching;
- - method of shield penetration.
All of them ensure the integrity and normal functioning of aboveground and underground facilities, reduce the time for laying communications, and reduce their cost.
Horizontal mechanical drilling
 Although this is one of the first methods of trenchless laying of communications, nevertheless, it is very often used now. This operation is often abbreviated as HDD (horizontal directional drilling), since this drilling is quite manageable in the earth.
Although this is one of the first methods of trenchless laying of communications, nevertheless, it is very often used now. This operation is often abbreviated as HDD (horizontal directional drilling), since this drilling is quite manageable in the earth.
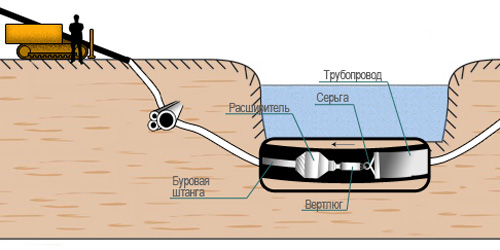
The horizontal drilling process can be divided into several stages. The first is drilling a pilot well. This is a very important operation, the location of the pipeline underground and the place of its exit depend on it. This is done as follows. The rock cutting tool is a drill head with a built-in emitter for locating. Also in the drill head there are holes for the exit of the drilling fluid supplied through the hollow rods. Thanks to the locator located at the operator, signals about its position, azimuth and slope are recorded from the drill head. Having on the display a diagram of other communications and objects and the trajectory of movement of the head, the operator manipulates the movement: first "stop", then measuring and changing the angle of the direction of movement, then again continuing the movement, but in a given direction. The direction of movement of the head changes due to the oblique cut on the head: the cut indicates the direction in which the head will go at the beginning of the movement after the drilling fluid is supplied.
After the head has exited at the point defined by the project, the next stage begins. The drill head is disconnected from the rods, and a reamer (rimmer) is connected, which, together with the rods, goes in the opposite direction. The rimmer has a diameter one and a half to two times larger than the diameter of the pipe. Rotating, it easily expands the pilot well to the required size.
A head with a swivel is attached to the retractable end of the pipeline. The pipeline is pulled in behind the rimmer, while the swivel is needed so that the pipe does not rotate according to the translational-rotational movement of the rimmer. Thanks to all these sequential operations, the pipeline lies exactly along the design trajectory.
Horizontal puncture
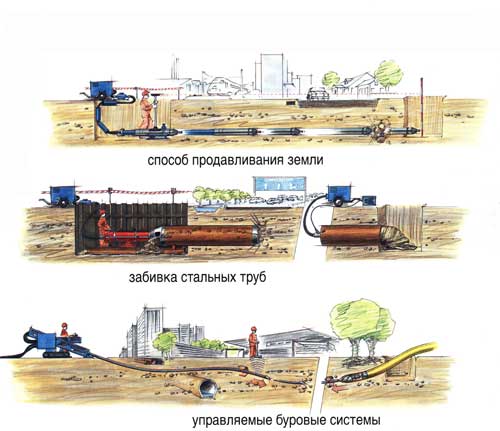
 Most often, punctures are performed under automobile and railways... At first, two pits are dug: starting and receiving. A frame with jacks is placed in the starting pit. The pipe to be laid is supplied with a tip, which makes it easier for it to pass through the ground. A pipe with a tip pierces the ground under the action of jacks. As soon as the open part of the pipe approaches the point of entry into the ground, the next section is attached to the pipe. The well around the pipe is compacted soil. Puncture speed and energy consumption depend on soil porosity, pipe material (different friction), hole size and puncture method. The types of puncture include hydro-puncture (a powerful stream of water is fed into the pipe) and vibration puncture (using vibratory hammers). Sometimes a puncture is made using a special mechanism - a pneumatic punch, inside the body of which there is a striker driven by compressed air. Due to the blows, the front end of the mechanism moves forward, while the friction of the body of the mechanism against the ground prevents the reverse movement. Low friction in swampy areas does not allow the use of a pneumatic punch there. He will not take rocks either, since he goes astray even in soft ground if he hits a stone. Punctured pipes are usually pulled with a diameter up to 426 mm for a length of 25-50 meters.
Most often, punctures are performed under automobile and railways... At first, two pits are dug: starting and receiving. A frame with jacks is placed in the starting pit. The pipe to be laid is supplied with a tip, which makes it easier for it to pass through the ground. A pipe with a tip pierces the ground under the action of jacks. As soon as the open part of the pipe approaches the point of entry into the ground, the next section is attached to the pipe. The well around the pipe is compacted soil. Puncture speed and energy consumption depend on soil porosity, pipe material (different friction), hole size and puncture method. The types of puncture include hydro-puncture (a powerful stream of water is fed into the pipe) and vibration puncture (using vibratory hammers). Sometimes a puncture is made using a special mechanism - a pneumatic punch, inside the body of which there is a striker driven by compressed air. Due to the blows, the front end of the mechanism moves forward, while the friction of the body of the mechanism against the ground prevents the reverse movement. Low friction in swampy areas does not allow the use of a pneumatic punch there. He will not take rocks either, since he goes astray even in soft ground if he hits a stone. Punctured pipes are usually pulled with a diameter up to 426 mm for a length of 25-50 meters.
Punching shear method
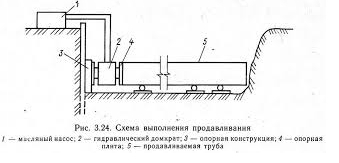 It is similar in many ways to the horizontal puncture method. Pits are also being dug, a frame and jacks are also being installed. But then the main difference begins: the pipe is not supplied, as with a puncture, with a tip, it is supplied with an open end. The pipe is equipped with a knife along the front edge, it is pressed into the ground by jacks that work cyclically, that is, forward and backward. When punctured, the soil moves apart, is pressed in and compacted around the pipe; when pressed, the soil enters the pipe with a plug. The soil from the pipe is removed manually or by mechanisms.
It is similar in many ways to the horizontal puncture method. Pits are also being dug, a frame and jacks are also being installed. But then the main difference begins: the pipe is not supplied, as with a puncture, with a tip, it is supplied with an open end. The pipe is equipped with a knife along the front edge, it is pressed into the ground by jacks that work cyclically, that is, forward and backward. When punctured, the soil moves apart, is pressed in and compacted around the pipe; when pressed, the soil enters the pipe with a plug. The soil from the pipe is removed manually or by mechanisms.
To facilitate the work, hydraulic washing and vibration impact units can be used. The combination of a water jet for soil erosion and an auger installation, which removes soil to the surface of the earth, greatly facilitates and speeds up the pushing process. This method allows you to lay pipes with a diameter up to 2 - 3 meters about 60 meters ... A shift usually takes about 10 meters.
Shield penetration method
 It is used in urban environments for tunnels and cylindrical adits, for driving underground lines. They are laid communication lines with a diameter of 2 to 10 meters.
It is used in urban environments for tunnels and cylindrical adits, for driving underground lines. They are laid communication lines with a diameter of 2 to 10 meters.
First, an assembly shaft is prepared, along which the shield is lowered into the face. Then work is carried out, which in the future will ensure the normal functioning of the tunnel: ventilation is arranged, electricity is supplied, soil removal systems are laid, the tunnel shield is mounted.
It is a steel shell, under the cover of which excavation and soil removal operations are carried out. Consists of the following parts:
- - front wedge-shaped;
- - supporting average;
- - tail rear.
In the front wedge-shaped part, work is carried out to loosen the collection and removal of soil. In the middle part there are jacks, which move the shield when driving. In the rear part, work is being carried out on the lining of the walls of the passed tunnel.
Benefits of trenchless technology
The growth of cities and the constant improvement of their infrastructure require constant changes in communication systems. And so that this process does not turn into a constant digging of streets, trenchless technologies for laying communications are used. They have a number of undoubted advantages:
- - mobility and compactness;
- - reduction in the cost of work due to the reduction in the timing of their performance
- - minimal damage, therefore, reducing the cost of restoring surrounding objects;
- - speed of work;
- - versatility of technology application (for pipelines, sewerage networks, drainage systems, etc.);
- - the ability to carry out work in specific conditions: under rivers and lakes, under existing roads and airfields, under floaters, even under the English Channel, that is, under the water column in rocks;
- - environmental friendliness of the process.
Aesthetics and ecology
 Endless ditches and trenches are not pleasing to the eye anyway, but what if, in addition, they are located in frequently visited places or recreation areas? Once in your life, you got out to look at the Cathedral of St. Basil the Blessed, and the road there was blocked by excavators and ditches dug by them. Well, how does it feel? How many conflicts arise, how many pickets are set up if a roaring bulldozer appears in an old public garden. Even if the earthmoving equipment does not uproot the tree, it will damage the root system. Often, after digging trenches, the level of groundwater drops, which is only harmful to the local flora, if not even leads to its disappearance. No matter how we separate the fertile layer and the parent rock during digging, when the trench is buried, the soil will mix, which leads to a change in the biocenosis. In the place of the former trenches, hillocks and dips appear due to precipitation and temperature changes, because it is impossible to achieve uniform compaction of the soil when filling the trench.
Endless ditches and trenches are not pleasing to the eye anyway, but what if, in addition, they are located in frequently visited places or recreation areas? Once in your life, you got out to look at the Cathedral of St. Basil the Blessed, and the road there was blocked by excavators and ditches dug by them. Well, how does it feel? How many conflicts arise, how many pickets are set up if a roaring bulldozer appears in an old public garden. Even if the earthmoving equipment does not uproot the tree, it will damage the root system. Often, after digging trenches, the level of groundwater drops, which is only harmful to the local flora, if not even leads to its disappearance. No matter how we separate the fertile layer and the parent rock during digging, when the trench is buried, the soil will mix, which leads to a change in the biocenosis. In the place of the former trenches, hillocks and dips appear due to precipitation and temperature changes, because it is impossible to achieve uniform compaction of the soil when filling the trench.

Trenchless laying of communications allows you to avoid violating the integrity of the environment, does not require funds for landscape restoration, the starting and finishing pits are point violations, in addition, inspection wells are installed in their place to control the pipelines.
More about oversized machinery, equipment and transport :
- Excavators. Complete classification.
In the article we will figure out in what cases it is useful and how trenchless pipe laying is carried out.
Why is this needed?
Actually, the trenchless method is of greatest value in two cases:
- When laying a new pipeline instead of a destroyed, damaged, overgrown or depressurized old one.
It is often much cheaper to run new pipes inside the old one with a decrease in diameter, or even destroy an old pipe in the ground and stretch a pipe of the same or larger diameter instead of it, than to dig and dismantle the old pipeline with the subsequent laying of a new one.
- In urban conditions, it is sometimes problematic to carry out excavations. To the cost of the actual excavation of the trench, indirect costs have to be added: relocation of transport routes, increased fuel consumption public transport, numerous agreements with organizations that own other communications at different depths in the area of work.
Trenchless laying, on the other hand, allows you to stretch the pipeline under a busy highway without stopping traffic and without disturbing lawns and road surfaces.

How it's done?
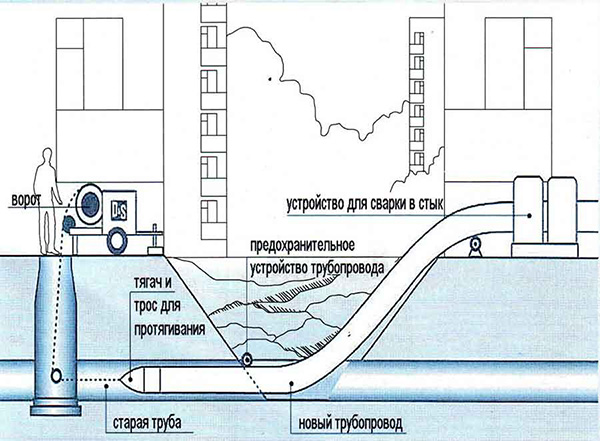
Laying a pipe of a smaller diameter inside the old
This is the simplest scenario. If, for example, a polyethylene pipe is laid instead of the old steel line of cold water supply, its smoother walls and the absence of overgrowth in the future provide at least not the worst permeability. The same goes for sewerage.
In this case, the main technological operations will be as follows:
- The old pipe is opened at two points. As a rule, one of them is a well.
- The winch is permanently mounted at one of the points. It must be securely fixed.
- A cable is passed through the pipe. There are a lot of ways, up to the flow of compressed air and the simplest parachute at the end of the cable.
- The winch pulls a ruff behind the cable to clean the pipe walls from debris and deposits.
- Then the cable is pulled into a long lash welded on the surface.
- Flanges are welded to it through plastic bushings.
- Shut-off valves are installed. You can run water.
Please note: for non-pressure water pipelines, it is also possible to lay a pipe from one point. The pipe is assembled on site from short modules that are connected by thread or soldering. As the assembly proceeds, the pipe is fed into the old one.
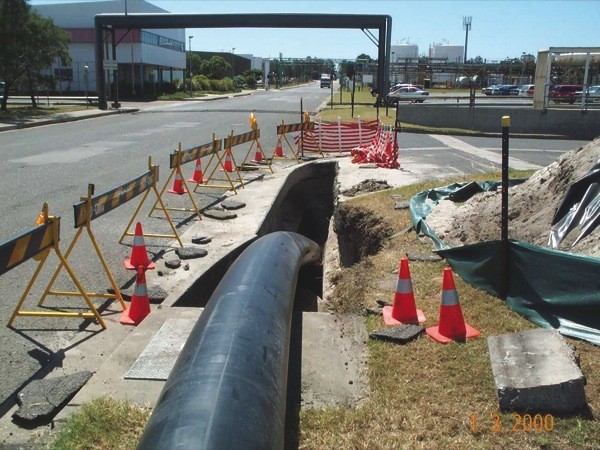

Laying a larger diameter pipe instead of the old one
This trenchless pipe repair requires slightly more sophisticated equipment. Typically a hydraulic calibrator and a pressure pump are used.
How it works?
- A cable is pulled through the old pipe;
- It pulls the calibrator to the beginning of the pipe section;
- Then a hydraulic pump supplies oil under high pressure to the delivery hose, after which the calibrator increases in diameter, tearing a section of the old pipe and pressing its remnants into the ground.
- The pressure drops, the calibrator decreases the diameter.
- The winch pulls it to the next section of the pipeline. Behind him is a whip of a new pipe.
Important: a huge advantage of laying a new pipe inside or instead of the old one is that such work does not require lengthy approval. After all, the plan of highways does not change, respectively, harm to other communications cannot be caused.
There is also an alternative method of breaking the old pipe: a pneumatic impact mechanism with a conical high-strength head is used. Each blow of the bumper pushes it forward, driving a few more millimeters of the old pipe into the ground.

Puncture of the soil with a shock-impulse pneumatic punch
In this case, the equipment for trenchless pipe laying is pneumatic. How does it work?
In fact, we are dealing with a kind of conventional jackhammer. Compressed air is blown into the hoses by the compressor; the control valve at a certain frequency sets the striker in motion, and he strikes the streamlined body, driving it into the ground.
The body is quite long (up to two meters, and in some cases even more). The device in the process of puncturing the soil is uncontrollable, and the success of the enterprise depends on the exact choice of direction at the start. For this, a so-called guide frame is used.
In principle, there are also controlled modifications of impact-impulse piercers; however, due to some technical problems of their execution, they have a relatively small size and performance.
Controlled pneumatic punches are used, as a rule, for a pilot puncture, after which an uncontrolled device of a larger caliber is launched in the same direction.

The main thing is to accurately aim at the target.
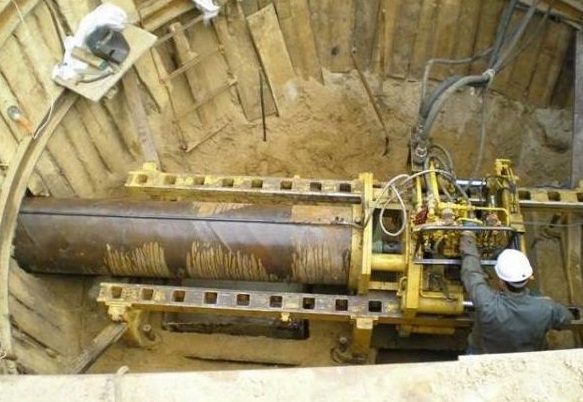
Punching pipe laying
This method boils down to the fact that the open end of the pipe is pressed into the ground; while the compacted core is removed from it with compressed air or a type of cutter with a feed auger.
Hydraulic jacks are used for indentation, which, of course, need support. The effort can be tens of tons. To reduce it, vibro-impact mechanisms are used that advance the pipe in short jerks.
The greatest advantage of this method is that it can be paved with it. In our country, punching of pipes with a diameter of up to 2500 mm was used; in world practice, there is experience in pushing pipes with a diameter of up to 3800 mm through the ground.

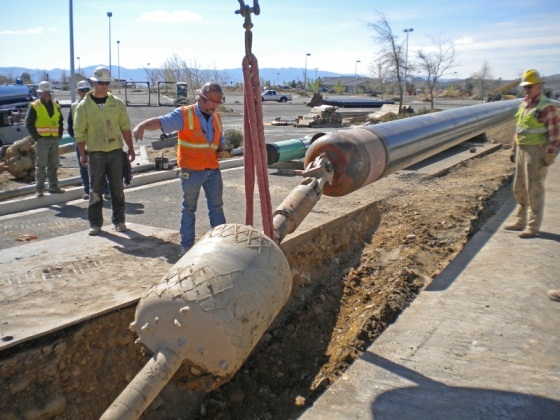
Directional horizontal drilling
In terms of time and resources, horizontal drilling is the most costly. However, it has a huge advantage. If all alternative methods either use an existing channel, or are able to pass only relatively soft soils, then soil of any strength, up to rocky, is subject to horizontal drilling.
What can you tell us about horizontal directional drilling (HDD)?
- To transmit torque to the drill, drill rods connected by peculiar hinges are most often used.
Remember, due to the location of the rig itself and the shape of the borehole, traditional drill pipes cannot be used. - Drilling hard soil requires, of course, the use of drilling mud. It has the function of lubricating while drilling, cooling the drill bit, stabilizing the borehole wall, and helping to remove drilling waste. The solutions usually need to be reclaimed and reused.
- Horizontal drilling is carried out at a speed of 1.5 - 19 m / h.
- The presence of groundwater puts an end to the use of horizontal drilling.

Distances
It can be pulled with a winch through an old pipe for a distance of up to half a kilometer. For all other laying methods, the maximum range is limited to 40 - 80 meters.
Conclusion
Don't forget, of course, that trenchless piping won't pay off in everyday household applications. If you want to connect to the water supply a private house- it will be much easier to hire an excavator or just arm yourself with a shovel. Good luck!
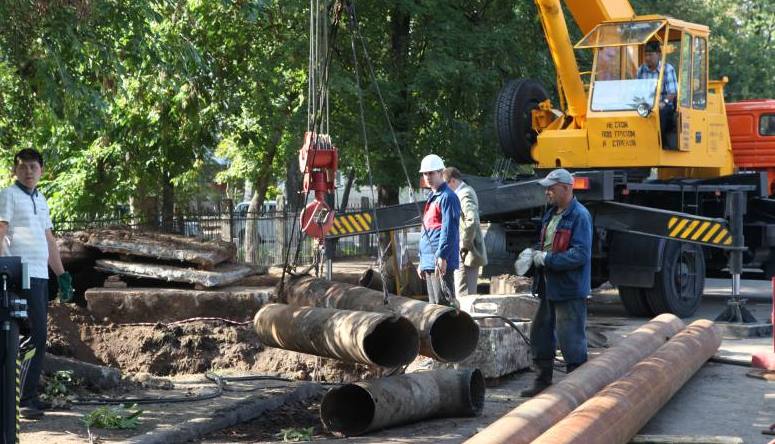
Many townspeople are painfully familiar with the picture: autumn is coming and a communal war begins on the streets with the main attributes - trenches and foundation pits. These gallant plumbers are trying to urgently save the city networks from the upcoming breakthroughs or "patch" the old cobwebs of pipes. But in Europe, they have long abandoned such urban excavations and switched to trenchless pipe laying, which is economically viable and does not disfigure appearance cities.
Trenchless installation preserves the road surface
Features of trenchless pipe laying
For many years, laying the pipeline in a trench has remained a common method of constructing urban communications. The consequences of these works are dug sidewalks and green areas, damaged roadways, altered public transport routes and constant indignation of the townspeople. Although all this nightmare can be avoided by using trenchless pipe laying technologies.
This is a closed method for the construction and repair of utilities, in which underground work is carried out without opening the ground. In this case, there is no need to build additional crossings, change traffic routes, carry out a large number of approvals with other utilities.

When trenchless pipelines are laid, 90% of the work is done underground.
Compared to laying a sewer pipe in a trench, the trenchless method involves the device engineering networks by the method of horizontal directional drilling, pipe punching, ground puncture, sanitation. This is the most promising way of building new and repairing or replacing old water supply and sewerage networks in a big city.
Method advantages
The main advantages of the method are understandable even to an ordinary person who is not indifferent to the appearance hometown.
- All communications that run near the pipeline remain unharmed. Indeed, when digging a trench, gusts of neighboring networks very often occur.
- The economic benefit is that there is no need to connect additional equipment and labor for excavation, backfilling of the pipeline trench .
- There is no need to make subsequent repairs to damaged asphalt, paving slabs.
- The speed of work.
- Ability to work in winter time.
- Preservation of the landscape, roadbed, green areas.
- Minimal harm to the environment.
- Emergency situations almost never arises.
The advantage of using the trenchless method is also that no special preparatory excavation is required. For example, laying polyethylene pipes in a trench involves the use of an excavator, a cushion of sand or gravel at the bottom. After laying, backfilling of the pipeline trench follows (SNiP makes special requirements for this stage of excavation), compaction and ramming of the soil. And in case closed way laying pipes requires only a well-designed work project, a well-thought-out optimal route without bends and turns, a calculated depth and slope of the pipeline.
Scope of use
The trenchless method of laying pipes is universal, since it can be used for different types communications. It is indispensable for the construction of pipelines under a busy highway, railroad track, subway lines, a river, as well as in conditions of dense running of other networks. It can be such communications:
- water pipes,
- sewerage,
- electric cables,
- pipeline,
- gas pipeline,
- communication cables.
Special equipment
To carry out such work, special equipment is required. Depending on which method of trenchless pipe laying is used for a particular engineering communication, are used
- drilling,
- hydraulic,
- location installations,
- generators,
- welding machines for plastic pipes,
- mortar mixing units,
- auto manipulators.

The soil is pressed through with a powerful hydraulic unit.
Basic methods
For trenchless pipe laying, the following most popular and demanded methods are used:
- reorganization,
- pushing,
- horizontal directional drilling,
It should be remembered that, as with open laying, it is imperative to adhere to the distance between the pipes in the trench established by SNiP, so also with the trenchless method, these rules must be observed.
The technology for trenchless pipe laying can be viewed here.
Sanitation
Translated from Latin means recovery, treatment. This procedure is used only on an already existing section of the pipeline and consists in replacing old pipes with new ones. This can be done in two ways - relining and renovation.
Relining is a common method of remediation, in which a new polyethylene pipe of a smaller diameter is laid in an old, for example, steel pipe. In this case, you need to carefully research internal state the old pipe, correctly select the diameter of the new one, at the end of which attach a hydraulic calibrator, which will move forward along the old line, making room for the new pipe.
Renovation is used if the old pipeline has outlived its usefulness, so it is completely destroyed, and a new one is laid in its place.
Punching
This method is used for large diameter pipes. At the same time, they are pressed into the ground using a hydraulic jack and a vibration shock mechanism. The soil, preferably sandy and loose, is removed by compressed air to the outside through the pipe itself.
Horizontal directional drilling
The most costly, but at the same time, the most versatile method of trenchless pipeline laying, since it can cope with soils of any density, even rocks, and lay a pipeline up to 100 meters long. The drilling process is carried out using installations for trenchless pipe laying - drilling machines. A small well is drilled at a depth of up to 15 m in a given direction. The drill head is connected to the drive rod, therefore, it is able to bypass underground obstacles, strictly adhere to a given trajectory. The resulting well is expanded and a working pipeline is pulled through it.

For trenchless pipe laying using the HDD method, drilling machines are used.
Ground puncture
This method is effective on clay and loamy soils, when it is necessary to lay pipes with a diameter of up to 15 cm. The essence of the method is that it is pushed through the soil steel pipe with a cone. The earth is not pulled out, but compacted with hydraulic jacks. A polyethylene pipe is then inserted into the formed well.

Trenchless pipelines are the future. We hope that we will soon forget about the unpleasant traces that remain from the repair work on heating mains and other city communications.





