In order to obtain the necessary indicators about the financial and economic activities of the enterprise, it is necessary to group the data contained in the primary documents in a certain way and generalize. This procedure is carried out using accounting registers.
Accounting register - a way to register, organize and display accounting information on tangible media.
The accounting registers are intended for the systematization and accumulation of data contained in primary documents accepted for accounting, and for the reflection of accounting information on accounting accounts and in financial statements.
Traditionally, accounting registers were represented by paper tangible media made in the form of tables. Under the conditions of using personal computers, the concept of an accounting register has been significantly expanded. Part of the information necessary for management is issued electronically as videogram. In this regard, a clear distinction is needed between the concepts of “accounting register” and “tangible medium” of accounting information.
In conditions of computer processing of credentials on the basis of the same material carrier (usually magnetic), several accounting registers can be obtained (printed).
Recording information about business transactions in accounting registers is called accounting registration. Accounting registration is an important and responsible area of \u200b\u200baccounting work. The quality of accounting depends on the correctness of the entries in the accounting registers of the data contained in the primary documents. In the conditions of automation of accounting, registration is implemented automatically.
Accounting registers classified according to the following main features:
1) in appearance;
2) by appointment;
3) by the degree of generalization or the volume of content;
4) in the form of construction.
1. In appearance Distinguish accounting books, car-points, free sheets, machinegrams, video programs.
Account books are tables firmly fastened together with a special graph. All pages in the book of accounts must be numbered, and in some (cash book), laced and sealed. On the last page of the book, signed by the head of the enterprise and the chief accountant, the number of numbered pages is indicated and a print is put. The advantage of books is that it is not possible to replace individual pages. The disadvantage is low mobility, only one person can work with books. It is impossible to group the data in the necessary section and apply at least partial automation of accounting work.
Cards - These are separate sheets of thick paper with a special graph. They come in standard sizes for easy storage in file cabinets. The advantage of card checks is their great mobility in terms of grouping data and accounting work. Partial metering automation can be used. Disadvantage - card replacement is possible.
Free sheets are separate sheets of non-thick paper with a special graph. Their difference from cards is in large sizes and storage methods. They are stored in folders. The use of free sheets is promising, since they can be filled and processed using personal computers.
Mashinograms and videograms - these are special registers obtained as a result of computer processing of accounting information. The information contained in them is grouped according to certain criteria with a subdivision into the results of various degrees: private, intermediate, general and summary. Mashinograms are obtained on paper in the form of printed tables, and by means of videograms accounting information is displayed on the monitor screen, i.e. the latter are its light display.
Currently, due to the widespread adoption of personal computers in accounting practice, there is a great similarity between machine programs and free sheets. The main difference may be that the registration on free sheets, as a rule, is done manually, and in machine programs - automatically.
2. By appointment accounting registers are divided into:
a) chronological;
b) systematic;
c) combined.
Chronological - these are registers in which entries are made in a calendar (chronological) sequence in order to control the incoming primary documents and identify the total amount of business transactions. An example is a registration journal or a register of documents. Conducting registration logs can be carried out both on paper and magnetic media with the display in the latter case of information in the form of videograms on the monitor.
Systematic registers are intended for recording business transactions that are homogeneous in economic content, as a rule, in accounting accounts. An example of a systematic record register is the General Ledger.
Chronological and systematic registers are kept in parallel and their results are periodically checked against each other.
Combined characterized by a combination of both chronological and systematic recordings. They appeared as a result of rationalization of accounting. An example of a combined register is an order journal.
3. By degree of generalization (volume of content) accounting registers are classified:
a) on synthetic;
b) for analytical;
c) for combined ones.
IN synthetic registers all entries are kept in a generalized form, usually in sum terms. An example is the Main Book.
IN analytical register registers are kept in more detail. They indicate the summary of the operation. Records in the registers of analytical accounting are kept in physical meters and in cash.
Analytical registers, in turn, are divided:
a) on contracting;
b) for quantitatively-total;
c) on multigraph.
Contract accounts are intended for the separate accounting of debit and credit turnover. These are, as a rule, books where personal accounts are opened for settlements with counterparties, and records are made in monetary terms.
Quantitative-total registers are intended for keeping records and records by quantity and amount. These registers are used for entries in the accounts of materials, finished products, goods, etc.
Multiple registers are designed to account for individual elements or items, which are understood as separate types of expenses. These are registers for the accounting of production costs and distribution costs.
IN combined registers combined synthetic and analytical accounting. As an example, magazines are warrants.
4. In the form of construction, the registers are divided into:
a) unilateral;
b) on bilateral;
c) on table;
d) for chess.
Single sidedthe registers on one side have columns reflecting the debit (receipt) of the account and the loan (expense). As an example, registers designed to take into account material values \u200b\u200bcan be used.
Bilateral registers differ from unilateral in that the debit part is on one (left) side of the expanded sheet, and the credit part is on the other (right). In bilateral registers, both parts have the same shape and the same indicators.
Schematically, the form of a unilateral register looks like this:
Bilateral Register Form
| Debit | Credit | ||||||
| date | Document No | Amount | date | Document No | Base (operation content) | Amount | |
Tabular or the multigraphic form of the accounting register is characterized by the fact that additional columns for transcripts are given for debit or credit.
Table register form
| date | Document Number | Base (operation content) | Debit | Credit | Including debit account | |||
Chess the form of accounting registers is designed to combine debit and credit records by applying special graphing vertically and horizontally. It makes it possible to reduce the number of records and combine analytical accounting with synthetic. According to the chess form, some order magazines are constructed.
Chess Register Form
| With credit bills | Depreciation | Materials | Salary | etc. | Total | ||
| To debit accounts | per month | since the beginning of the year | |||||
| Account Number (name) | Record Base | ||||||
| Depreciation | Fig. 2. General scheme of classification of accounting registers |
Economic operations after their completion should be reflected in accounting. In order to obtain the necessary information about economic activity, all the data contained in the primary documents should be grouped in accordance with their economic content on the accounts. Such recording of accounts is carried out in the accounting registers. The reflection of business transactions in accounting registers is the second stage of accounting work.
Accounting registers - these are special tables (forms) for reflecting in them business transactions recorded in primary documents.
Registers are intended for accumulation, grouping and systematization of homogeneous business transactions contained in documents in accounts, serve the purposes of control, management and analysis of financial and economic activities of organizations and are used to compile established reporting forms.
Due to the fact that there are many accounts and registers, a large number of accounting registers are classified:
by purpose and amount of information (volume of content): synthetic, analytical, combining synthetic and analytical accounting;
by account type : chronological, systematic, combined;
in appearance : free sheets, cards, books, machinegrams;
by structure (graphene form) : unilateral, bilateral, multigraphic;
on a material basis : paper and paperless registers.
Registers synthetic accounting designed to record business transactions on synthetic accounts. Entries in these registers are kept without an explanatory text, in a generalized form and only in monetary terms.
Registers analytical accounting designed and used to reflect homogeneous transactions in separate analytical accounts. Each operation is recorded quite fully, not only in monetary terms, but also in kind.
Registers combining synthetic and analytical accounting , increase the reliability and visibility of accounting. In these registers, separate lines are intended for analytical accounting, and the total data of all records are indicators of synthetic accounting.
Chronological Registers are used to record operations in chronological order, i.e. in the order they were made (most often in the order that documents were received by the accounting department) without grouping them into accounts.
IN systematic registers homogeneous business operations are systematized according to the accounts of synthetic and analytical accounting. An example is a general ledger in which the turnover for all synthetic accounts is recorded with the corresponding accounts.
Combined registers combine chronological and systematic recording.
Free sheets (statements) are single sheets or several stapled sheets. These are order books or statements. They open for a month. Some have liners. Stored in folders.
Cards - These are also free sheets, but not fastened together. They are stored in boxes in a specific system. The collection of homogeneous cards for the purpose is called a card index.
Account books are used to record business transactions on both synthetic and analytical accounts. In the books, all the sheets are laced, numbered, sealed with a seal and signature. The book is issued at the beginning of the year and is conducted during it.
Mashinogram - accounting register obtained by processing documents on a PC. Their forms are diverse and depend on the purpose and content of the objects considered in them.
An important step in the formation of reliable accounting information is business registration technique . The reflection of business transactions in the accounting registers should be carried out in a certain order on the basis of executed and processed documents.
Recording business transactions in registers is called post operations . Posting is made on the basis of affixed correspondence of accounts on documents (account assignment of documents).
Certain account methodswhich can be classified according to the following criteria:
by the nature of the record : unigraphic and digraphic;
to systematize : chronological, systematic, combined (synchronistic);
by image : in the form of a formula, in the form of a diagram (using "T" accounts), in the form of a matrix;
by number of copies : simple (disposable), copy (reusable);
by filling method : manual and machine records.
Unigraphic record is only one-way recording, i.e. a business transaction is recorded only on debit or only on credit of the account (single entry). Unigraphic records are used for accounting on off-balance accounts, which reflect the property temporarily held by the enterprise and not owned by it.
Digraph characterized by the fact that each business transaction is reflected in the debit of one and the credit of other accounts (double entry). In accounting practice, digraph records, depending on the relationship of the offsetting accounts, are divided into the following types:
Simple accounts characterized by the fact that the debit of one account and the credit of another account reflects the business transaction in the same amount. IN complicated account the debit of one account can correspond with credits of several accounts or, conversely, the credit of one account - with debits of several accounts. In this case, the sum of the entries for the debit and credit of different accounts should be equal. Reversal notes are correction records produced by the red reversal method. These entries are widely used in accounting practice. Reverse records are used to correct incorrectly indicated correspondence of accounts by changing the places of debit and credit. However, in practice such records are not widely used, since they overstate accounts.
Accounting registers - this is an integral part of the organization’s accounting, used to systematize and save the data of primary accounting documents.
Accounting accounting registers are designed to reflect business transactions in the accounts of accounting. Previously, information from accounting registers was a trade secret.
Forms of accounting registers
Until 2013, the forms of accounting registers were uniform and mandatory for use by all business entities.
These forms were presented in the Albums of Unified Forms. Currently, the forms of accounting registers are approved by the head of the enterprise.
However, the law provides a list of mandatory information contained in the registers:
- register name;
- name of the business entity filling out the register;
- the period of compilation or maintenance of the register;
- chronological or systematic classification of accounting objects;
- unit of measure and currency of operation;
- an indication of the posts responsible for maintaining the register;
- Name and signature of responsible persons.
Forms of accounting registers are established by law and can be taken from official sites, they can be downloaded from the Internet, look for using search engines.
Classification of ledgers

Accounting registers are classified by purpose, generalization of information and type. By appointment, the registers are divided into
- chronological
- systematic
- synchronistic (combined).
The chronological registers record facts of economic activity as they occur. Examples of chronological accounting registers are registers and various registers.
Data in chronological and systematic registers complement each other
Systematic registers are filled in for certain accounts, which include business transactions. An example of a systematic register is the balance sheet.
If the register includes a chronological and systematic record, then it refers to combined synchronous registers. An example of such an accounting register is the Journal-Home.
The use of synchronous registers makes the information in them more visual.
Thus, the sum of revolutions in chronological registers is equal to the revolutions for debit or credit of systematic registers. This dependency is called the Mendes rule.
According to the generalization of information, registers are divided into synthetic and analytical.
- In synthetic registers, transactions are recorded only with the date and amount.
- Analytical accounting registers are accounting forms in which analytical information is systematized, that is, not only the details of the operation, but also its brief content.
Business entities also use integrated accounting registers, combining the principles of synthetic and analytical registers, as well as chronometric and systematic factors.
When using such forms, the totals for synthetic and analytical accounts automatically coincide, which eliminates the need for additional reconciliation of revolutions for different statements.
In appearance, the registers are divided into books, cards, blank sheets and machine media
- A book is a register that is necessarily laced up, numbered and sealed with the seal and signatures of responsible persons.
- A card is a register in the form of a typewritten table.
- A blank sheet is a register in the form of a table to be hemmed. To keep records of cards and blank sheets, registers are kept to exclude the spoofing of the register or, if necessary, to restore the lost document.
- Machine medium is an electronic document stored on a magnetic medium and certified by an electronic signature. When using machine media, information should be printed in a timely manner.
The accuracy of the information reflected in the accounting registers is provided by responsible persons.
If an error is detected in the register, the correction is made by the responsible person indicating the date of the correction and sealed with his signature.
Correction is made by striking out the wrong information once so that it remains readable. Correct data is indicated above.
For each correction in the registers, written explanations of the responsible person must be given.
Accounting Register Sample Document Turnover Scheme 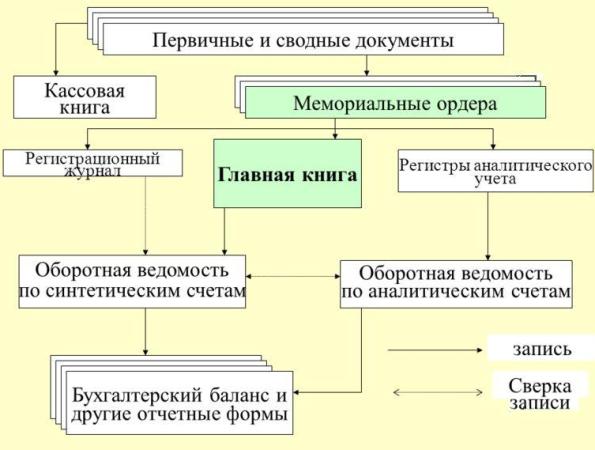
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
The primary documentation received by the accounting department is subject to verification both in form and in content. The accuracy and completeness of registration, the presence of mandatory details, the legality of recorded operations, the logical relationship of indicators are assessed. After that, registration and grouping of data is carried out. Information is recorded in a system of analytical and synthetic accounts. For this purpose, accounting registers are provided: accounting forms. Let us consider further what they can be.
General information
Accounting registers are special counting tables. They are formed according to the economic grouping of information about property and sources. Forms of accounting registers are necessary to reflect ongoing business transactions on the relevant accounts.
Classification
Existing types of accounting registers are subdivided according to purpose, appearance and method of data generalization. According to the first criterion, documents are distinguished:
- Systematic.
- Chronological.
- Combined synchronous.
Chronological accounting registers are documents in which records of facts of economic activity are made as they are carried out, without other systematization. These include, for example, registries. In the systematic tables, entries are made according to grouping characteristics - accounts. Information from these two types of registers should complement each other. Therefore, the sum of revolutions according to chronological documents is always equal to the sum of credit / debit indicators from systematic tables. When both chronological and systematic entries are entered in the same register, then it is considered combined (synchronistic).
Summary of Information
On this basis, accounting registers are divided into differentiated and integrated. The consideration of data can be carried out inductively, that is, to the general from the particular. In this case, the integration of information takes place. Also, generalization can be carried out deductively: to the quotient of the general (from reporting to primary documentation). In this case, there is a differentiation of information.
Appearance
According to this criterion, the following accounting registers are distinguished:
- Books. They are a document, specially cut out in a special way, laced up, bound and signed by a responsible person (Ch. Accountant).
- Cards. They are forms printed as tables.
- Free sheets. Such accounting registers are tables placed on letterheads subject to brochure. Such sheets are considered an alternative to books and cards. These papers are stored in folders. For them, as for cards, registries should be kept.
- Machine carriers. These accounting ledgers have technical features. The data are placed in this case not on paper, but on electronic media (storage).
Consider the main accounting registers separately.

Books
These registers contain information on facts of economic activity (operations). It is distributed in accordance with the specifics of the objects. Books must be designed in accordance with the requirements of the rules. In addition to being bound, laced, and numbered, the number of pages should be indicated on the back of the last sheet. Under the indicated number are signed by the head of the enterprise and Ch. accountant, stamped. Typically, books are used in cases where the objects of observation are in small quantities. But for a number of categories (for example, cash transactions), enterprises keep records in the cash book, where all events are recorded. The general ledger generalizes all objects.

Cards
This is a fairly convenient form of registers. They can be sorted, they differ in visibility and accessibility when handling. Externally, the cards may be different. The most common types include: contracting, multi-columned and inventory. The first are filled on the one hand, since the columns for debit and credit are located next to each other. The presence of parallel columns allows you to see the status of the settlement operations of the enterprise. Material values \u200b\u200bare taken into account in inventory cards. They enter the column "Residue". It reflects the amount of funds remaining after the registration of a business transaction. Therefore, in each account there are columns for income, expense and balance. The heading is the standard (limit) for stock. Its presence allows you to easily determine whether these funds are present in the enterprise in a larger quantity than is expected. If it turns out that there are fewer of them, then the difference with the limit is established. In multi-column cards, the operations of the economic life of the company are taken into account with the allocation of components in columns. This, for example, is relevant for cases when a fact is recorded in complex amounts, that is, payment of various expenses of the company is reflected.

Free sheets
They are larger than cards in size. Accordingly, the volume of information reflected in them is also increasing. In accounting practice, free sheets represent different statements. They are used to summarize homogeneous data. For example, they reflect depreciation on fixed assets, vacation (shipment) of goods, and so on.
Machine carriers
They can be floppy disks, disks, etc. When using such registers, the enterprise must produce paper copies of documents. This is done, including at the request of the authorities authorized to exercise control, as well as the court and the prosecutor's office. Media features determine the order of information. Their use is determined by the mass of operations, the specificity and volume of objects of accounting and other factors.

Conclusion
The correctness of fixing business transactions in the accounting registers is ensured by the persons who compiled and signed them. During the storage of such documentation, it is necessary to protect information from unauthorized correction. Corrections to errors in accounting registers must be justified and confirmed by the signature of the employee who made the changes. In this case, the correction date must be indicated. In accordance with the Federal Law "On Accounting", the information contained in the registers is classified as a trade secret. Persons who have access to such documentation are required to keep it. For disclosure of information violators are responsible in accordance with the norms of domestic law.
perform the functions necessary for any company: fixing, grouping, storage of information about economic facts. The number of items is quite large, which is explained by the peculiarities of accounting for various objects and facts of business activity in doing business.
Categories of accounting registers and forms
Accounting registers act as a basic tool for summarizing data from the primary documentation used in the future to make entries in the relevant accounts and to form indicators of financial statements. Recording in accounting registers, the specialist not only carries out processing of the primary documentation, but also analyzes the content of the business transactions confirmed by them for the legality and correctness of the display of actual events.
Depending on the method of data capture accounting registers classified:
- on systematic - allow you to collect information regarding accounting accounts, to such, in particular, include the general ledger;
- chronological - are intended for continuous recording of data in the order of receipt of documents without a breakdown by areas of accounting, these include various magazines and books;
- combined - combine the ability to group data in chronological order, they include the magazine-orders and statements.
Depending on the data order for accounting registersthe following breakdown is provided:
- filled out on one or two sides of the sheet;
- chess sheets - with data located in the tables at the intersection of rows (for debit of account) and columns (for credit of account).
By the nature and method of summarizing information, the following list of accounting registers:
- Analytical - serve to accumulate analytical information on the accounts of the synthetic accounting of the company, with their help, the movement of material assets, the timeliness of settlements with partners, etc. are tracked.
- Synthetic - allow you to get the final, final, not detailed data on the amounts collected on the accounts. These include the main book.
- Combining the functions of the above types of registers, they are characteristic for journal order system accounting.
If you evaluate the appearance accounting ledgers, then among them we can distinguish:
- Card forms - are sheets with blank tables printed on them, which include contract accounts, multi-column and inventory, for example a card for fixed assets accounting.
- Magazines, books - bound, unfolded sheets in hard or soft cover, on which, as a rule, the name and period of filling out the register are indicated. Pages like accounting registers they are numbered, laced up and fastened on the last sheet, where the chief accountant's signature is put.
- Large format sheets - reminiscent of enlarged cards; these include accounting records and some order journals.
- Automated printed registers - are created using specialized electronic accounting databases, based on the information accumulated in them.
List of most frequently used registers
At the moment, most unified forms of accounting registers are not required to use. This is confirmed by the information distributed by the RF Ministry of Finance dated 04.12.2012 No. ПЗ-10/2012 in connection with the entry into force of amendments to the Law "On Accounting" dated 06.12.2011 No. 402-ФЗ. However, this rule does not apply to individual forms put into effect by specially authorized bodies. The only requirement for registers was the availability of a list of mandatory details in the forms developed by companies.
Registries, books, cards put in place within the company must be mentioned in the accounting policy of the company, and those forms that the chief accountant and his subordinates will use must be approved by the head of the organization. Companies whose source of financing is the state budget, and also the state is the main shareholder, are required to use the forms in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n. Commercial organizations, in turn, quite often create their own forms based on forms from the order.
To illustrate the above, we provide an excerpt from the above order:
|
Cards intended for accounting: |
|
· Fixed assets; |
|
· Groups of fixed assets; |
|
Sheets: |
|
· Turnover balance; |
|
· Negotiable for non-financial assets; |
|
· Accumulation of data. |
|
· home; · Analytical accounting of deposited salary amounts. |
|
· Accounting for transactions in various accounts; |
|
· Accounting for the movement of other property. |
|
· Cards; |
|
· Transfer of documents; |
|
· Accounting of securities; |
|
· Deposited amounts; |
|
· Capitalization and write-offs on expenses. |
|
Cards: |
|
· Multiline; |
|
· Accounting of funds and settlements; |
|
· Accounting for loans; |
|
· Control over the movement of values; |
|
· Fixing payment documents for execution. |
|
· Inventory cards for accounting OS; |
|
· Inventory. |
|
Sheets: |
|
· Deviations based on the results of the inventory; |
|
· Registration of unbilled deliveries. |
How to draw up an order on approval of registers - sample
To confirm the legitimacy of the application of forms must be issued order to approve accounting registerscompany. The main form designer and sample accounting registers acts as the chief accountant of the company, and confirms their head of the organization.
This regulatory document will necessarily be required by the inspectors from the Federal Tax Service during the audit. Based on the order types of accounting registersreviewers will request forms of interest to them. Although today most accounting processes are carried out using electronic databases, in paragraph 6 of Art. 10 of Law No. 402-ФЗ contains a clear indication of the need to store registers in printed and signed form or in digital format with the obligatory presence of a digital signature. Based on this, the forms requested by the tax authorities will have to be formed in paper form or in electronic format, but with the necessary signature.
In most cases, the specific name of the register is indicated for each account. For this, special tables are created in which the account, the name of the form and the person who is responsible for its regular execution are indicated. An example is the following variant of such a table.
An example of fixing accounting registers in an organization order or accounting policy
***
The presence of registers that provide comprehensive accounting of property and liabilities is mandatory for the full functioning of the accounting of any organization. Without them, it will not be possible to prepare final financial statements for all interested users. Also, this information is used to provide statistical data, managerial accounting and current analysis of the results of the company.
Companies not belonging to the state and budget sectors are allowed to develop their own forms of such documents. They must be approved by the head of the organization and they must contain all the required details from the list established by law. State-owned companies are required to use standardized forms approved by the RF Ministry of Finance for these purposes. In most cases, the latter serve as the basis for private companies to create their own accounting forms.