IN last years The question of acceptance tests is very acute. Many believe that the standards in our country are used on a voluntary basis, and the technical regulation does not provide direct instructions on the need for acceptance tests. There are also such judgments: why to invest extra funds, if you still need to issue a certificate. Or: permission to use can not be received, acceptance tests are also an excess procedure, etc.
Let's try to figure out.
Technical Regulations
From mid-February 2013, a document was entered into force, which was waiting for a long time: "On the safety of machines and equipment" Tr Ts 010/2011. It is prescribed direct instructions on safety guarantee during design work and subsequent manufacture. That is, the conversation is that it is necessary to determine and set the risk permissible for the machine and / or equipment. At the same time, the level of security must be provided:
- complex calculations and tests that are based on proven methodological developments;
- completeness of development and research works;
- making machine and / or equipment must be accompanied by tests prescribed in the attached design (project) documentation.
That is, it is clear that both the project organization and the manufacturer are obliged to test the object. They are provided for project documentation, they must be implemented before certification (procedures confirming compliance). The fact of declaration is obvious - the availability of a document on its own tests carried out before the confirmation procedure. But it is not clear which tests are meant.
The concept of "test"
It means a technical action that makes it possible to check the engineering characteristics of the object (product), determine the degree of wear, quality and suitability for long-term use. Testing a prototype is allowed both in individual elements and in the complex.
Test steps
Allocate departmental, interdepartmental and government acceptance tests. GOST 34.601-90 Sets the following types:
- preliminary;
- experienced;
- remote.
Any one requires compliance with a specific procedure for which a special document is developed - the program of acceptance tests. She must approve the customer. The program prescribes the volume of tests, and both the necessary and sufficient, providing the assigned completeness of the results obtained and their accuracy.

Preliminary tests should be carried out after testing and pre-debugging equipment.
Experienced tests are held in order to determine the readiness of equipment (machines, systems) to permanent operation. Without these tests, acceptance tests are prohibited.
Finishing stage
These are acceptance tests. It depends on the ticket to the life of the equipment being developed (machines, systems). This stage gives answers to questions set in front of the designers. First of all, it is a correspondence of the specified intended purpose, performance and feasibility efficiency, whether it will meet the modern safety requirements and contribute to the improvement of labor workers.
Even during acceptance tests check:
- assessing the success of the experienced tests passed;
- deciding on the possibility of launching equipment (machines, systems) into industrial operation.
Acceptance tests are carried out at the customer's facility (and already existing). For this, an order is issued or an order to execute the necessary work.
Both of these documents are written according to current provisions and standards developed for certain types of objects. They are approved by ministries churring designing organizations.
The program is prescribed in detail:
- the purpose of the upcoming works and their volume;
- acceptance criteria for both the object as a whole and its parts;
- the list of objects to be trials, as well as a list of requirements that the object must comply with (necessarily with indications of the items of the technical task);
- terms of testing and timing;
- material and metrological provision of upcoming work;
- test Tests: Technical and Organizational;
- methods for holding acceptance tests and processing results obtained;
- the names of those appointed by those responsible for conducting test work;
- list of necessary documentation;
- checking its quality (mainly operational and design).
Depending on the technical and other characteristics of the research object, the document may contain specified sections, but if necessary, they can be reduced or new ones.

Package of documents for program development and techniques
Requirements for the design and content of these documents are governed by GOST 13.301-79.
The list of documents for the creation of the program and the technique is not constant. It changes depending on the relationship of the object being tested to that or ministry or organization. But in general, the following documents will be required:
- manual;
- regulatory - technical documentation: technical conditions, standards, etc.;
- passport of the object being received;
- documents on the registration from the manufacturer's company;
- drawings and descriptions;
- protocols of factory tests (for foreign manufacturers).
Compiled and certified program and methods of test work by the customer and specialists of Rostechnadzor are registered in the Federal Agency.
Commission
For acceptance tests, it is formed by the appropriate decree of the enterprise. The Commission should include representatives of the supplier of components, a customer, a design organization, a developer, technician organs and organizations engaged in assembly and commissioning work. The Commission shall be approved by the Commission.
In his work, the Commission uses the following documents:
- technical task for creating equipment (machines, systems);
- protocol preliminary tests;
- executive documentation for installation;
- remote Test Program;
- acts of metrological certification (if necessary);
- working logs with experienced tests;
- acts of acceptance from them and completion;
- technical documentation for equipment (machine, system).
Before acceptable tests, system documentation and technical are finalized according to the comments of the Protocol for conducting preliminary tests and the act on the completion of experienced tests.

The manufacturer's enterprise and the design organization must provide an acceptance commission:
- materials conducted preliminary tests;
- experienced facilities, successfully past preliminary tests;
- reviews, expert opinion, patents, copyright certificates decorated in the process of displacement testing;
- other materials approved by test techniques for certain types of objects and typical programs.
Check
This is one of the main points of acceptance tests. They should not duplicate the previous stages, and the timing of them are compressed.
Acceptance tests include checking:
- quality and completeness of the implementation of equipment functions (machines, systems) in accordance with the terms of reference;
- work personnel in dialogue;
- execution of any requirement related to equipment (machine, system);
- completeness of operational and accompanying documentation, and their quality;
- methods and means required to restore the performance of the object after possible failures.
If two or more objects have similar characteristics, the same conditions are created for testing.
During the acceptance tests, studies are not conducted on durability and reliability, but the indicators obtained during the tests should be entered into relevant acts.
Test ending
Acceptance tests are completed by technical expertise. That is, the object is disassembled, and the technical condition of its elements (nodes) is set, as well as the complexity of disassembly and assembling the entire object of the study.
At the end of work, the Commission develops and constitutes the protocol of tests. On its basis there will be acceptance. If necessary, the Commission defines the amount of improvement of equipment (machines, systems) and / or technical documentation, and also gives recommendations on the launch of an object being tested into mass production.
If this is not possible, the act of conducting acceptance tests is complemented by proposals for improving the product, re-acceptable testing or requirement for termination of work on the object.

Acts and results
The acts of acceptance of the object approves the management of the enterprise that appointed a commission for testing.
The technique of acceptance tests recommends that if necessary, consider the results of the tests carried out on the scientific and technic focus of the profile ministry or enterprise developing an object together with the customer (that is, even before approving the acceptance act).
The decision to launch tested objects in a series is made on the basis of materials and recommendations of the Acceptance Commission and / or Scientific and Technical Council by the Order by the Ministry. It necessarily indicates the volume of production, and recommendations are made to implement.
Act of acceptance tests
Four years ago, unified forms of primary documents were canceled. This gave organizations the right to develop their own templates of any document. The main thing is to comply with the following requirements:
- Subscribes a document by all the persons with its own. If one of them is proxy, it must be reflected in the act.
- It does not affect the legality of the act, it is decorated on the usual sheet of paper scripts or on a branded form. As, by the way, the document is written or recruited on the hand (the main thing is "live" signatures).
- Stamps and prints are put on the document, if it is spelled out in the Charter and / or accounting policy of the Organization.
- Logically, the act has three parts: the beginning (the so-called header is the date, name, place of compilation), the main part and conclusion.
The number of copies of documents is equal to the number of sides signatory. Each of them has the same legal status and identical text. Information about the act is entered into a specialized journal of accounting documentation of the organization.
Errors and descriptions in the document on acceptance tests should not be. Because it may not only be the basis for setting an object to the balance of the organization or his write-off, but also the main confirming document when contacting the lawsuit in the court.
The center of the page is written the name of the document, below - the place of drawing up (city, village, etc.) and the date.

The main part of the act contains the following information:
- Composition of the Commission. It is indicated by the enterprise (organization, ministry), representatives who will sign the document, further their posts and full surname, name and patronymic.
- Name of the object and real address His mounting.
- Detailed drawn list of test work (drawn up in the form of a list or table) with information on the conditions of testing.
- In case of detection of flaws, as well as elimination proposals are made either below or draw up an application to the act.
- The act of acceptance tests (sample is given below) ends with the conclusions of the Commission on the capacity or the incapacity of the subject's test.
The opinion of any member of the Commission, different from the rest, is necessarily prescribed either in the act of act (separate item), or in annex to it. All accompanying paper members are also listed in it.

And only after that, all participants in the preparation of the document put their signatures and decipher them.
Completion of work
The signed act is included in the document accompanying the object that takes tests. Act is stored either in accordance with the current legislation or in the manner prescribed by the regulatory acts of the organization.
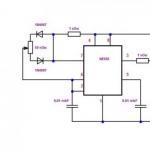
Testing electronic equipment It is called experimental determination of parameter values \u200b\u200band product quality indicators in the process of operation or when playing certain impacts on the equipment according to the specified program. Tests are one of the most important and final stages of production, because According to their results, judged on the operational reliability of the product.
Tests can be control - In order to control the quality of products and research, conducted to establish dependencies between the maximum permissible values \u200b\u200bof the product parameters and the values \u200b\u200bof the operating modes called boundary.
In terms of holding Tests are divided into normal and accelerated. Accelerated Call tests that provide information on quality indicators in a shorter period than in normal operating conditions. They can be forced and abbreviated. Forced Tests are based on the intensification of processes that cause failures or damage by increasing the loads (temperature, pressure, velocities, etc.). Abbreviated Tests ensure a decrease in the timing of tests by obtaining additional information outside the test, applying extrapolation and other methods without intensifying the reasons for failures.
By the method of testing distinguish tests destructive and non-destructive.
Tests are carried out on stages of production and operation . There are tests of prototypes and products manufactured by serial. The main task tests of prototypes It is the most complete identification of the compliance of their technological and operational characteristics, the requirements of technical conditions. According to the results of these tests, called acceptance, decide on the feasibility of introducing prototypes into mass production. In this regard, tests are carried out very carefully according to an extended program with rigid modes and long-term impacts of various climatic and mechanical factors. For prototypes and products of single production, tests of the following types are used: preliminary, convective, departmental, interdepartmental, state (licensed). Preliminary (control) tests Experienced products are carried out to determine the possibility of their presentation on acceptance tests. Contracting tests Apply in the process of product development to assess the impact of changes made to it in order to provide the required quality indicators.
Products manufactured by serialsubjected to control tests, receiving and complete, periodic, typical and attestation.
Acceptance tests The aim of checking the compliance of manufactured products with the requirements of technical conditions. Periodic tests are carried out in cases where specifications It is impossible to determine in the receiving tests. Periodic tests allow you to monitor the maintenance of product quality at the required level. Typical tests Finished products are carried out before, and after making changes to the design or manufacturing technology in order to verify the effectiveness of changes made or comparing product quality issued at different times. Typical tests should be carried out according to the program that ensures the comparability of test results before and after changes. Attestation tests Serve to assess the quality level of products. Tests of two or more products performed in identical conditions for comparing the characteristics of their quality are called comparative.
The type of control tests are estimated. They are carried out for such an assessment of product quality, in which it is not required to determine the values \u200b\u200bof its parameters.
Control tests can be solid or selective. In case of continuous tests, each product is checked, and only a part and the received data from the received data are judged by the affordability of the entire party. When developing selective control, it is necessary to establish the number of product tests, test duration and acceptance number (IF). Under the inverter understand the greatest number Defective products in the sample, in which the test results can be considered positive. If the number of defective products is greater than the PC, the test results are considered negative. In the latter case, two solutions are possible: Continue control or rejoice the entire batch, which can be subjected to a continuous check or returned to the manufacturer (Contractor).
The probability of acceptance of the batch of products, the quality of which does not correspond to the established permissible percentage of defective products (DPDI), are called the risk of the customer (RZ). In agreement between the customer and the manufacturer, an acceptable level of quality (CC) is established. The probability of resting the batch of products, the quality of which corresponds to the Criminal Code, is called the risk of the manufacturer (RI).
The volume and sequence of tests of products is determined by the test program and technical requirements for a specific product. The main requirement for products subjected to climate, mechanical and electrical tests is to save the output (checked) parameters after testing within the limits established by the specifications.
Products before testing must undergo monitoring and step by step. Masting reduces the likelihood of failures caused by hidden production defects. Traveker significantly extends the production cycle, but increases product reliability. It is very important to establish time and modes (thermal and electrical) to perform this operation.
8. Types and methods of testing
8.1. Vida tests.
To verify the NCU compliance with the requirements of this standard, the following tests are carried out:
- typical tests;
- acceptance tests.
The list of checks and tests is shown in Table 7.
Note - Types of Test NCU and their names are accepted in IEC 439-1-85. For national economic products in accordance with GOST 16504, the following types of tests are envisaged: qualification, periodic, commercial and typical. Program of typical tests in IEC 439-1-85 is the basis for establishing programs of any control tests on the NCU.
Requirements, for frequency, test volumes and acceptance rules set in Appendix R.
8.1.1. Typical tests (8.2).
Typical tests are intended to verify the NCU compliance with the technical requirements of this Standard.
Typical tests are carried out on one or more types of NCU. Typical tests of some species are allowed to be carried out on parts of the NCU. Tests and checks are allowed to be carried out in any order and / or on various samples.
Typical tests are also carried out in whole or in part when introduced into the design of the NCU changes that may adversely affect the technical characteristics of the NCU.
Table 7. List of checks and tests conducted on the NCU.
| Name of inspections and testing | room |
| 1. Typical tests | |
| 1.1. Check the limit values \u200b\u200bof the temperature exceeding | 8.2 |
| 1.1.2. Verification of dielectric properties | 8.2.2 |
| 1.3. Checking short circuit strength | 8.2.3 |
| 1.4. Protective Ground Efficiency Performance | 8.2.4 |
| 1.5. Checking air gaps and leakage tracks | 8.2.5 |
| 1.6. Checking mechanical performance | 8.2.6 |
| 1.7. Check degrees of protection | 8.2.7 |
| 1.8A. Operation and performance check | 8.2.8A. |
| 1.9A. Check for vibration resistance and seismic resistance | 8.2.9A. |
| 2. Recommendant tests | 8.3 |
| 2.1. Inspection of the NKU | 8.3.1 |
| 2.2. Dielectric tests | 8.3.2 |
| 2.3. Checking the electrical continuity of the chain of the protective grounding | 8.3.3 |
| 2.4. Checking insulation resistance | 8.3.4 |
| 2.5. Operation and performance check | 8.3.5A. |
In coordination between the consumer and the manufacturer, additional typical tests associated with the NCU test for compliance with special requirements are allowed (by 6.2).
8.1.2. Recommendant tests (8.3).
Recommendant tests are subjected to each NCC manufactured in order to detect defects in materials and in manufacturing technology.
Tests are allowed to be carried out in any sequence.
8.1.3. Tests of devices and individual components embedded in the NCU.
Typical and receiving tests are not carried out for devices or individual components embedded in the NCU, if their choice was made in accordance with the requirements of 7.6.1, and the installation is carried out according to the manufacturer's instructions.
8.2. Typical tests.
8.2.1. Check the limiting values \u200b\u200bof the temperature exceeding.
8.2.1.1. General.
The purpose of the test is to check the limit values \u200b\u200bof the temperature exceeding for compliance with the requirements of 7.3 for different parts of the NCU.
The test is usually carried out at rated values \u200b\u200bof the current in accordance with 8.2.1.3 on the assembled NCU.
Tests are allowed to be carried out using resistors as heaters with an equivalent loss power in accordance with 8.2.1.4. It is allowed to test individual parts (panels, boxes, shells, etc.) of the NCU (according to 8.2.1.2) when making measures that ensure the reliability of the results.
Tests of individual chains on temperature exceeding should be carried out by a current for which the chains are intended, and at the corresponding frequency. The voltage values \u200b\u200bfor the test should be so that through the circuits passed the current equal to the one in 8.2.1.3. Rated voltage should be supplied to the relay coils, contactors, releasers and similar elements.
An open type NCU is not tested for an excess of temperature, if, according to the results of typical tests of individual parts or by crossing of wires and the placement of the devices, it is obvious that during operation it will not be excessive to exceed the temperature and equipment, connected to the NCU, and parts from the insulating material will not be damaged.
8.2.1.2. Location NCU. NCU must be installed in the same way as at the site of operation - with all elements of the shell, etc.
When testing individual parts or structural blocks, neighboring parts or structural blocks should create the same temperature conditions as during normal operation. At the same time, resistors can be used as heaters.
8.2.1.3 Tests for excess of temperature under conditions when all the equipment is under voltage.
Tests should be carried out on one or more characteristic compounds of the chains of this NCU in order to obtain with sufficient accuracy to get the maximum possible value of the temperature. The test circuit is loaded with a rated current (by 4.2), multiplied by the coefficient of simultaneity (by 4.8). If there are fuses in the NCU, then when testing, they should be supplied with fusible inserts corresponding to the manufacturer's instructions. Power loss in fused inserts applied in tests should be reflected in the test protocol.
The size and location of the external wires used in the test should also be reflected in the test protocol.
The test should be carried out over time sufficient to increase, temperature to a constant value (as a rule, this time does not exceed 8 hours). Almost this condition is performed when the temperature changes not more than 1 ° C / h.
Notes
1. In order to accelerate the tests, if the instrument allows it, the current can be increased in the first part of the test, after which it is reduced to the installed test value.
2. If during the test includes a coil of the device in the control circuit, then the temperature is measured when the thermal equilibrium is reached both in the main chain and in the coil of the control goal. In the absence of detailed information regarding external conductors and operating conditions, the cross section of external test conductors should be selected in accordance with 8.2.1.3.1-8.2.1.3.4.
8.2.1.3.1. With the values \u200b\u200bof the test current up to 400 A:
a) for compounds should use single-core copper cables or insulated wires whose cross sections are shown in Table 8;
b) how practically it is perfect, the conductors should be opened openly;
c) the minimum length of each temporary connection between the clips must be:
- 1m - for the wire with a cross section of up to 35 mm2.
- 2M- for the wire with a cross section of sv. 35 mm2.
Table 8. Standard sections of copper wires corresponding to test current, current in amperes
| Test current range | S, mm2 | Nominal current value * |
| SV 0 to 7.9 | 1 | 6 |
| > 7,9 >15,9 | 1,5 | 8, 10,12 |
| »15.9» 22 | 2,5 | 16, 20 |
| »22» 30 | 4 | 25 |
| »30» 39 | 6 | 32 |
| »39» 54 | 10 | 40, 50 |
| »54" 72 | 16 | 63 |
| »72" 93 | 25 | 80 |
| »93" 117 | 35 | 100 |
| "117" 147 | 50 | 125 |
| "147" 180 | 70 | 160 |
| »180" 216 | 95 | 200 |
| "216" 250 | 120 | 250 |
| »250" 287 | 150 | - |
| »287» 334 | 185 | 315 |
| »334» 400 | 240 | 400 |
| * Recommended standard current values \u200b\u200bare given only for references. | ||
8.2.1.3.2. With the values \u200b\u200bof the test current of St. 400, but not more than 800 A:
a) the conductors should use stranded copper cables with polyvinyl chloride insulation, whose cross sections are given in Table 9, or equivalent copper tires specified in Table 9, selected in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations; |
b) Copper cables or tires should be located at a distance approximately equal to the distance between the clips. Copper tires must have a black and matte surface finish. Parallel cables connected to one clamp should be grouped together and are located at a distance of about 10 mm from each other. Parallel copper tires connected to one clamp should be located at a distance of each other, equal to their thickness.
If the dimensions specified for the tires cannot be supplemented, the use of other tires having close to the value of the cross section, as well as approximately the same or smaller cooling surfaces. Between cables and copper tires, the space should not be filled;
c) for single and multiphase tests The minimum length of any temporal connection to the voltage source must be 2 m. The minimum length when connecting the star can be reduced to 1.2 m.
8.2.1.3:3. With the values \u200b\u200bof the test current of St. 800, but not more than 3150 A:
a) Copper tires with sections specified in Table 9 should be used as conductors, except for the case when the NCU is calculated only with cables. In this case, the size and location of the cables indicates the manufacturer;
b) Copper tires should be located at distances, approximately equal distance between the clips. Copper tires must have a black and matte surface finish. Parallel copper tires attached to one clamp should be located at a distance equal to about their thickness.
If the dimensions specified for the tires cannot be supplemented, the use of other tires having close to the value of the cross section, as well as approximately the same or smaller cooling surfaces. Between copper tires, the space should not be filled;
c) for single and multiphase tests The minimum length of any temporal connection to the voltage source should be 3 m, but can be reduced to 2 m, provided that the temperature at the end of the area connected to the voltage source will be no more than 5 ° With below excess, temperature in the middle of the connecting section. The minimum length when connecting the star can be reduced to 2 m.
Table 9. Standard sections of copper conductors corresponding to the test current.
| Nominal current value, and | Range of test values, and | Test conductor | |||
| Cable | Copper tire | ||||
| Number | Section, mm2 | Number | Dimensions, mm. | ||
| 500 | From 400 to 500 | 2 | 150 | 2 | 30x5 |
| 630 | St. 500 "630 | 2 | 185 | 2 | 40x5 |
| 800 | "630" 800 | 2 | 240 | 2 | 50x5 |
| 1000 | »800" 1000 | 2 | 60x5 | ||
| 1250 | »1000" 1250 | 2 | 80x5 | ||
| 1600 | "1250" 1600 | 2 | 100x5 | ||
| 2000 | "1600" 2000 | 3 | 100x5 | ||
| 2500 | »2000» 2500 | 4 | 100x5 | ||
| 3150 | "2500" 3150 | 3 | 100x10 | ||
Notes
1. The rated current should be greater than the first value and less or equal to the second test value.
2. It is assumed that the tires are mounted vertically. Horizontal installation is used when it is determined by the manufacturer.
8.2.1.3.4. With the values \u200b\u200bof the test current exceeding 3150 A, an agreement must be concluded between the manufacturer and the consumer, according to all the appropriate test conditions, such as the type of food, the number of phases and frequency (if necessary), the cross section of test conductor, etc., this information should be Refilled in test report.
Note - The use of single-phase alternating current to test multiphase NCUs is allowed in cases where magnetic effects are so weak that they can be neglected.
8.2.1.4. Tests for excess of temperature carried out using resistors as heaters with equivalent loss power.
For closed NCUs of some types, the main and auxiliary chains of which are relatively small minimum currents, the loss power can be mimic with the help of resistors that create the same amount of heat and placed in the appropriate places inside the shell. The cross sections of the conductors attached to these resistors should be such that outside the shell has not distinguished the significantly noticeable amount of heat. Tests carried out using resistors are considered typical for all NCUs having the same shells, even if different equipment contains various equipment, provided that the sum of the power loss power supply, taking into account the coefficient of simultaneity, does not exceed the value obtained during the test.
The heating temperature of the built-in hardware should not exceed the values \u200b\u200bshown in Table 3 (7.3). It can be calculated approximately. To do this, the heating temperature of this apparatus, measured in the open air, to supplement the difference between the temperature inside the shell and the air temperature surrounding the shell.
8.2.1.5. Measuring temperature.
For temperature measurement, thermometers and thermocouples should be used.
For windings, the method of measuring temperature changes in resistance changes are usually used.
To measure the air temperature inside the NCU, several measuring instruments should be installed at convenient locations. Thermometers and thermocouples must be protected from air flow and thermal radiation.
8.2.1.6. Ambient temperature.
The ambient air temperature should be measured in the last quarter of the test period with at least two thermometers or thermocouples, which are evenly placed around the NCU at an altitude of 1/2 height of the NCU, and at a distance of about 1 m from the NCU. Thermometers and thermocouples must be protected from air flow and thermal radiation.
If the ambient air temperature during the test is 10 to 40 ° C, the values \u200b\u200bshown in Table 3 (7.3) are the limit values \u200b\u200bof the heating temperature.
8.2.1.7. Test results.
At the end of the tests, the temperature exceeds should not be greater than the values \u200b\u200bshown in Table 3 (by 7.3).
The instrument should work satisfactorily at the values \u200b\u200bof the voltage within the limits permitted for it at a given temperature inside the NCU.
8.2.2. Checking dielectric properties.
8.2.2.1. General.
For those parts of the NCU, which have already passed typical tests in accordance with the technical conditions, the test of dielectric strength is not carried out if the dielectric strength of these parts has not deteriorated during the installation.
The test voltage must be applied between:
a) all current-time parts and connected by open conductive parts of the NCU;
b) each pole and all other poles connected to conduct this test with the open conductive parts of the NCU connected.
If there is a protective conductor in the NCU, isolated from open conductive parts according to 7.4.3.2. d), then this conductor should be considered as a separate chain, i.e. it should be tested at the same voltage as the main chain to which it belongs.
Test voltage at the time of its application should not exceed 50% of the values \u200b\u200bgiven in 8.2.2.4. After that, it increases evenly within a few seconds to the full value specified in 8.2.2.4, and is withstanding for 1 min.
AC sources must have sufficient power to maintain test voltage regardless of any leakage currents. The test voltage should have a practically sinusoidal waveform and frequency from 45 to 62 Hz. 8.2.2.2 Tests of shells made from insulating material.
For shells made of insulating material, an additional test of dielectric properties should be carried out between the test voltage apply between the metal foil imposed on the outer side of the shell on the holes and joints, and the currently connected circuit parts and open conductive parts that are located inside the shell and are located next to holes and joints.
When testing, the voltage must be 1.5 times the values \u200b\u200bshown in Table 10.
8.2.2.3. External handles of controls from insulating material.
For controls of controls from insulating material or coated with insulating material in accordance with 7.4.3.1.3. The dielectric properties should be tested by an application of voltage, 1.5 times higher than the test voltage indicated in Table 10, between the current-time parts and metal foil wrapped Around the entire surface of the handle.
During this test, the metal structures should not be grounded or connected to any other chain.
8.2.2.4. Test voltage value.
The test voltage value should be as follows.
8.2.2.4.1. For the main chain, as well as for auxiliary not specified circuits, not agreed 8.2.2.4.2., - according to Table 10.
Table 10, in Volta.
8.2.2.4.2. For auxiliary chains, which are not directly attached to the main chain, according to Table 11.
Table 11.
8.2.2.5. Test results.
The product is considered to be sustained the test if there is no breakdown or overlap on the surface.
8.2.3. Check the short circuit strength.
8.2.3.1. NCU circuits not subject to tested for short circuit.
Checking the short circuit's strength is not conducted.
8.2.3.1.1. For NCU with a nominal expected short circuit current no more than 10 ka.
8.2.3.1.2. For NCU protected by current-limiting devices with a shutdown current not higher than 15 when the nominal disconnecting ability.
8.2.3.1.3. For auxiliary chains, intended. For connectivity to transformers, the rated power of which does not exceed 10 kV and at a nominal secondary voltage of at least 110 V or 1.6 kV and at a nominal secondary voltage of less than 110 V, in which the relative short circuit voltage is not less than 4 %.
8.2.3.1.4. For all parts of the NCU (main tires, tire supports, connections with tires, input and output blocks, switching vehicles, etc.), previously typical tests.
8.2.3.2. NCU chains that should be tested for short circuit. Tests for strength with a short circuit are subject to chains that are not mentioned in 8.2.3.1.
8.2.3.2.1. Test preparation. NCU or part of it must be listed in a state corresponding to normal operation.
Except for tire tests and depending on the type of kit design, it suffices to test only one functional block, provided that the remaining functional blocks have a similar design and cannot affect the test results.
8.2.3.2.2. Testing. General.
If the test chain contains fuses, then you should use fuse inserts to the maximum rated current and, if required, the type indicated by the manufacturer. Conductors for the power of the NCU and the short-circuited compounds used in the NCU test must have sufficient strength to withstand a short circuit, and to be placed in such a way as not to create additional loads.
The test chain must be joined to the fashionable NCU clamps.
Three-phase NCUs must be attached to the input clips of the NCU. Three-phase NCUs must be connected to three-phase chains.
Except for checking the nominal briefly withstand current and nominal shock current (by 7.5.2.1.2a), the value of the expected short circuit current at a supply voltage, equal to 1,1 nominal working voltage, should be determined according to the calibration oscillogram, which is removed during short-range power conductors. Cutting is carried out by connecting as close as possible to the supply input of a small resistance. From the oscillogram, it should be seen that until the operation of the protective device or for a predetermined period, the current has a relatively constant nature approaching the value specified in 8.2.3.2.4.
When testing on alternating current, the frequency in the test chain must be equal to the nominal frequency with the deviation of about 25%. The test chain should include a reliable device (for example, a fuse made of copper wire with a diameter of 0.1 mm and a length of at least 50 mm) to detect emergency current and, if necessary, also ohmic resistance to limit the intended emergency current to 100a.
8.2.3.2.3. Testing the main chain of the NCU containing the teams of the tires must be subject to the test indicated in the transfer A), b), d).
NCUs that do not contain teams of tires are subject to the test indicated in Listing a).
NCUs that do not meet the requirements 7.5.5.1.2 are subject to an additional test indicated in the enumeration of B).
a) If the output circuit contains a block, which was not previously tested, the following test should be carried out:
To test the output circuit, the corresponding exhaust clamps must be equipped with a bolted short-circuit compound. The switching device must be closed and in a closed position as under normal operation, after which the test voltage is submitted once, which is kept for a time sufficient to respond to a short-circuit protection device in the output block and its shutdown; In any case, the duration of the supply voltage supply must be at least 10 periods;
b) NCU containing main tires should be subjected to an additional one-time test in order to verify the strength of the short circuit of the main tires and the incoming chain containing any compounds. The point in which a short circuit creates should be at a distance (2 ± 0.40) m from the nearest power supply point. When checking the nominal brief summary current (by 4.3) and the nominal shock current (4.4), this distance can be increased. If the length of the NCU tires is less than 1.6 m, then the short circuit must be carried out at the end of these tires. If the bus assembly consists of various sections (it is characterized by a cross section, the distance between adjacent tires, type and number of supports per 1 m), then each section should be experienced separately or together with others if the conditions listed above are performed;
c) A short circuit is achieved using a bolted connection on the conductors connecting the tires to one output unit as close as possible to the clamps from the tires of the output block. The short-circuit current value should be the same as the main tires;
d) If there is a neutral bus, it must be subjected to one-time test for checking the short circuit with respect to the nearest phase bus containing at least one compound. When connecting a neutral tire with this phase bus, the requirements specified in 8.2.3.2.3b should be performed. In the absence of a special agreement between the manufacturer, and the consumer value of the test current in the neutral bus should be 60% of different test current.
8.2.3.2.4. The value and duration of the short circuit current.
a) NCU with a short-circuit protective device included in the input unit (7.5.2.1.1).
The current corresponding to the specified expected short circuit current must proceed until it is turned off by a protective device;
b) NCU, which does not contain a short-circuit protective device in the input unit (7.5.2.1.2).
For NCU with a nominal briefly withstand current and nominal shock current, electrodynamic and thermal resistance should be checked by these rated currents. The test of briefly withstand current (by 4.3) is allowed to be carried out at any corresponding voltage, the active value of which is determined by the oscillogram.
Notes
1. If necessary, the duration of the test may be different, while the test current i must be changed according to the i2t \u003d const formula, where, the time during which the test is carried out, provided that the calculated impact value does not exceed the nominal impactary current and that active value Briefly withstand current will not be lower than the nominal value at least in the same phase for at least 0.1C after switching on.
2. Tests with shock currents and testing briefly withstand current can be carried out, separately. In this case, time T, during which tests of short circuit current I should be carried out, it should be such that the i2t value does not exceed the equivalent value defined in the tests of briefly withstand current, but it must be at least three periods.
The test can be carried out at any appropriate voltage with tire heating to any suitable temperature. The highest shock value of the current during the first test cycle should be at least the nominal shock current (by 7.5.3).
For NCU with nominal anticipated short circuit currents, nominal short circuit currents or short-circuit rates, disconnected fuses (3.5-4.7), electrodynamic and thermal resistance should be checked by the expected short circuit current from the power side of the protective device used, if any . The value of the expected short circuit current is equal to the value of the short-circuit conditional current or the short circuit current value, turned off by the fuse.
8.2 3.2.5. Test results.
After the end of the test, the deformation of the conductors should not be observed. A minor shin deformation is permissible provided that the requirements for air gaps and leakage tract lengths are performed. There should also be any signs of destruction of insulation of conductors and carrier insulating parts, i.e., the main characteristics of insulation should remain so that the mechanical and electrical insulating properties of the equipment meet the requirements of this standard. There should be no weakening of parts used to connect the conductors; Conductors should not be disconnected from the output clamps.
The deformation of the shell is permissible to the extent that the degree of protection does not deteriorate and the air gaps are not reduced below the permissible.
Any deformation of tires or metal structures, disturbing the normal entry of removable and retractable parts, should be considered as damage.
In cases where the permissibility of the deformations arising for doubt, it is necessary to confirm that the equipment included in the NCU is in a state that meets the requirements of the relevant technical specifications.
8.2.3.2.6. In coordination between the consumer and the manufacturer, short-circuit resistance can be checked by extrapolation based on the results of typical tests of such devices or settlement path.
8.2.4. Check the effectiveness of the chain of protection.
8.2.4.1. Check the reliability of the connections between open conductive parts of the NCU and the protection chain.
The check should be carried out in order to obtain confirmation of the reliability of the connection of various open conductive parts of the NCU with a security chain in accordance with the requirements of 7.4.3.1.
The electrical resistance value of the protective ground circuit should be checked between the clamp for the input protective conductor and the corresponding open conductive part of the NCU.
8.2.4.2. Testing the strength of the protection chain at short circuit currents.
To carry out the tests, you need to connect a single-phase test power supply system to the input clamping of a single phase, and the output phase clip and the output protection conductor clamp of the output block.
If there are several conclusions blocks in the NCU, then each unit should be tested separately by the block clamp and the clip of the corresponding output protective conductor. Each tested output unit must be equipped with a protective device that skips the maximum value of the shock current and I2T. Testing with a protective device located outside the NCU is allowed.
When tested, the metal structures of the NCU should be isolated from the ground. The values \u200b\u200bof the expected current and the applied voltage should be single-phase values \u200b\u200bobtained according to the tests of the NCU for strength to three-phase short circuits.
All other conditions for this test are similar to those listed in 8.2.3.2
8.2.4.3. Test results.
The test results are considered positive if continuity is not broken and the strength of protection chain is stored after passing the short circuit current, regardless of whether this circuit presents a separate conductor or metal.
Test results are confirmed by visual inspection and measurement of the transmitted current equal to the nominal current of the corresponding output block.
Notes.
1. When used as a protective conductor, the metal struck is allowed and local heating in places of compounds, provided that the electrical continuity does not deteriorate and the sunbathing of adjacent elements is excluded.
2. Condition by note. 1) must be performed due to a comparative check before and after testing the resistance measured between the clips for the input and output protective conductors.
8.2.5. Check air gaps and leakage paths.
Air gaps and leak path lengths must comply with the requirements of 7.1.2.
The value of air gaps and leak path lengths should be checked to measure linear dimensions, taking into account possible deformations of individual elements of the design of the NCU, including any changes from the action of dynamic shocks at short circuit currents. If the NCU contains retractable parts, then checking air gaps and leak path lengths should be performed in the working, test and disconnected positions of these parts.
8.2.6. Checking mechanical performance.
Checking for mechanical performance are not subjected to components that have passed typical tests according to the corresponding technical conditions On them, provided that the mechanical characteristics of the components did not deteriorate during installation.
Parts subjected to typical tests must be checked for mechanical triggering with the number of operating cycles 50. In the NCU with retractable function blocks, one cycle includes moving the block from the attached position to the disconnected and back.
Test results are considered successful if the performance of the devices, blocking and similar devices did not deteriorate.
8.2.7. Check the degree of protection.
The degree of protection on 7.2.1 should be verified for compliance with the requirements of GOST 14254.
Test methods other than GOST 14254 must be consistent with the consumer.
8.2.8A. Check for functioning and efficiency.
For functionally completed NCUs, a functioning should be carried out. Check are carried out according to the program and methodology prepared by the developer concept.
Performance checks are carried out for all NCUs.
8.2.9A. Check for vibration resistance and seismic resistance.
Check for vibration resistance and seismic resistance are carried out according to GOST 16962.2.
8.3 Recommendant tests.
8.3.1 Inspection of the NCU.
Inspection of the NCU includes:
- check the mechanical triggering of components, locks, clamps, etc.;
- checking the correctness of the guide of the conductors;
- visual inspection in order to identify the presence of the required degree of protection;
- checking the values \u200b\u200bof air gaps and leakage paths;
- verification of screw and bolt connections for the presence of the corresponding contact; Selective check is allowed;
- checking the completeness of information and marking on 5.1 and 5.2. h is also the correspondence of the NCU this data;
- verification of the NCU compliance with electrical principal schemes and / or schemes of compounds and other technical documentation on the NCU.
8.3.2. Dielectric tests.
Dielectric tests should not be carried out on the NCU, the insulation resistance was tested in accordance with 8.3.4.
8.3.2.1. General.
Test voltage in accordance with the requirements 8.2.2.4. must be submitted for 1 seconds. AC source must have sufficient power to maintain test voltage regardless of all leakage currents. The voltage should have a practically sinusoidal waveform and frequency from 45 to 62 Hz.
During the test, all the electrical equipment of the NCU should be connected, except that, according to the appropriate specifications, is designed for a lower test voltage, and the hardware consuming (for example, windings, measuring instruments) and in which the applied test voltage can cause Current flow must be disabled. This equipment should be disconnected from one of its clamps. If the instrument is not calculated on the full voltage, all clamps must be disconnected.
Capacitors that serve to eliminate interference, installed between the current-time parts and open conductive parts, do not disconnect; They must withstand the test tension.
For this test:
- all switching devices must be closed or test voltage must be supplied sequentially on all parts of the chain;
- The test voltage must be applied between the current-time parts and the metal structures of the NCU.
8.3.2.2. Test voltage value (8.2.2.4).
If the equipment included in the main or auxiliary chain to be tested, dielectric tests have previously passed, the test voltage should be reduced to 85% of the value specified in 8.2.2.4.
8.3.2.3. Test results.
The product is considered to be sustained the test if there has not been a breakdown of isolation or overlap over the surface.
8.3.3. Check the protection and electrical continuity of the protection chain.
Checks are subject to means of protection against direct and indirect touch to the current parts. The protection chains must be verified for compliance with the requirements of 7.4.3.1.5.
Checking protection chains, including, includes verification, as a rule, selective, bolted compounds in terms of providing the necessary contact press.
8.3.4. Check insulation resistance.
For NCU, which were not tested on the electrical strength of isolation according to 8.2.2 and 8.3.2, it is necessary to measure the insulation resistance. These measurements should be carried out using a non-voltage of at least 500 V.
Tests are considered satisfactory if the insulation resistance between current-time circuits and conductive parts will be no lower than 1000 Ohm per 1 in the nominal voltage of these chains relative to the Earth.
8.3.5A. Check for functioning and efficiency.
For functionally completed NCU, in coordination between the consumer and the manufacturer, a functioning and performance can be carried out. The verification is carried out according to the program and methodology of the developer of the electrical concept, coordinated with the manufacturer.
In the absence of such a program, the following checks should be carried out:
- correctness of the connections and labeling of the NCU, wires, cables, tires, devices, devices and devices using electrical installation indicators;
- triggering devices, devices and devices.
All tests are classified according to the following principles: the appointment, level of conduct, the development phase, testing of finished products, conditions and place of conduct, the duration, the result of the impact determined by the characteristics of the object (Fig.).
Fig. Test classification by type
3.1 Depending on the purpose of the test, it is possible to divide into research, determination, comparative and control.
Research tests are carried out to study certain characteristics of the properties of the object and their goal are:
determination or assessment of performance indicators of the functioning of the subject under certain conditions of its application;
select the best operating modes of the object or the best characteristics of the properties of the object;
comparison of many options for implementing an object in design and certification;
constructing a mathematical model of the functioning of an object (assessment of the parameters of the mathematical model);
the selection of material factors affecting the quality of the functioning of the object;
selection of the species of the mathematical model of the object (from the specified set of options).
A feature of research tests is the facultivative nature of their holding, and they, as a rule, do not apply during the delivery of finished products.
Determinatory tests are carried out to determine the values \u200b\u200bof the characteristics of the object with the specified values \u200b\u200bof accuracy and reliability indicators.
Comparative tests are carried out to compare the characteristics of the properties of similar or identical objects. In practice, sometimes there is a need to compare the quality similar in characteristics or even the same EA, but manufactured, for example, by various enterprises. For this, compared objects in identical conditions are experiencing.
Controls and experts are carried out to control the quality of the object. Tests of this species constitute the most numerous test group.
3.2 The objectives and tasks of the tests change as the product of the stages of the "life" cycle passes. In this regard, it is clear to the allocation in the classification of the test groups under the design and manufacture of finished products.
At the design stage, convection, preliminary and acceptance tests are carried out.
Types of finished product tests include qualifying, presenters, commercial, periodic inspection, typical, certification, certification.
Promotive tests are research tests carried out in the design of products in order to assess the impact of changes made to it to achieve the specified values \u200b\u200bof quality indicators.
Preliminary tests are control tests of prototypes and (or) experienced product batches in order to determine the possibility of their presentation on acceptance tests.
Acceptance (MVI, GI) tests are also controlling tests. These are testing experienced samples, experienced parties of products or products of single production, conducted to solve the issue of the feasibility of producing this product (EA) on the production and (or) use of it for its intended purpose.
Qualification tests are carried out already at the installation series or the first industrial batch of EA, i.e. At the stage of development of the production of EA. The purpose of them is to evaluate the availability of the enterprise to the production of products of this type in a given volume.
Bearer test EA must be carried out by the technical control service of the manufacturer before presenting it for acceptance by the customer's representative, a consumer or other acceptance authorities.
Recommendant tests are carried out in developmental production. These are control tests of manufactured products during receiving control.
Periodic test products are carried out with \\ purpose of controlling the quality of product quality and the possibility of continuing its release in the amount and within the time limits established by the regulatory and technical documents (NTD). This type of control testing is usually carried out every month or a quarter, as well as at the beginning of the production of EA at the factory and during the resumption of production after its temporary termination. The results of periodic tests apply to all parties issued for a certain time. Periodic tests include such tests under which part of the EA resource is produced (long-term vibration, multiple blows, thermal cycles); These are relatively expensive tests, so they are always selective.
Inspection tests are a special type of control test. They are held in a selective order in order to control the stability of the quality of established types of products by specially authorized organizations.
Typical tests are control tests of manufactured products carried out in order to assess the effectiveness and expediency of made changes in the design, recipe or technological process.
BUTtestational .andexperts are held to assess the level of product quality in its certification by quality category.
Certification tests are control tests of products carried out in order to establish compliance with the characteristics of its properties by national and (or) international NTD .
3.3 Depending on the duration, all tests are divided into normal, accelerated, abbreviated.
Under normal the tests of EA are understood as tests, methods and conditions of which ensure that the required amount of information on the characteristics of the object properties at the same time interval as under the conditions of operation.
In turn accelerated tests are such tests, methods and conditions that provide the necessary information on the quality of EA in a shorter period than with normal tests. In NTD, the values \u200b\u200bof the influencing factors and operation modes corresponding to normal test conditions are indicated on the methods of testing specific types of EA. Abbreviated tests are carried out on a reduced program.
3.4 Depending on the level of significance of tests, EA can be divided into state, interdepartmental and departmental.
TO state tests include the tests of the established most important types of EA, conducted by the Head Organization for State Tests, or acceptance tests held by the State Commission or the testing organization, which is given the right to conduct them.
Interdepartmental tests are the tests of EA, held by the Commission from representatives of several interested ministries and departments or acceptance tests of established types of EA for the acceptance of its compound parts developed by several departments.
Departmental tests are held by the Commission from representatives of the Ministry of the Ministry or the Office.
3.5 EA tests in accordance with external affecting factors are divided into mechanical, climatic, thermal radiation, electrical, electromagnetic, magnetic, chemical (exposure to special environments), biological (impact of biological factors).
Obviously, not all external impacts can be imitate, and they, as already noted, can not always be applied together, as happens in real conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to establish what external impacts should be exposed to what will be the level, the frequency, the sequence of changing these effects, as well as the duration of the operation of the EA in various modes. When choosing external affecting factors when testing EA, it is necessary to consider:
type of equipment that uses equipment (ground, aircraft, maritime, etc.);
the level of testing of the test object (radiotechnical complexes and functional systems, electronic equipment, radio-electronic blocks, components, materials), depending on which the number of external actors selected for testing can decrease or increase;
climatic area of \u200b\u200bsubsequent operation of the test object;
terms of use for the purpose, transportation and storage of the test object.
3.6 Tests are called destroy if in the process they are used by destroying control methods or affecting an external factors lead to its unsuitability for further use.