Bookmark this site
The control of the meters is carried out by the consumer himself, with whom a service contract has been concluded. If the communication systems through which water is supplied to the object and discharged into the sewer system are equipped with measuring instruments, then the consumer no longer needs to calculate the water consumption depending on the time of year or day. Objective data obtained automatic system, eliminates the possibility of any disagreements between customers and suppliers, representatives of local communication services.
If the technical measuring instruments are not installed by the client or they are faulty and do not have seals, then the amount of water consumed by consumers is determined according to the throughput of communication services facilities. These points are spelled out in every contract concluded between contractors and consumers.
The above conditions for the lack of accounting for the readings of a private meter also include cases of unauthorized connection to the water supply system and illegally organized wastewater systems.
Payment methods for water supply services
If you have a counting device on the water supply system, then the readings taken from it remain to be multiplied by the tariff. Separately, it is necessary to calculate the volumes for hot and cold water supply, since their tariffs differ. The amounts received are added up, and the consumer pays for services at the point of receipt of payments or through the machine, in accordance with the actual amount, which includes value added tax.
As for the drainage of those consumers who are in contractual relations with contractors, and these are the owners of private houses, privatized apartments, their calculation of drainage will be slightly different. They will have to pay for this service based on the standards approved by the local authorities, which are adopted according to the average indicators of water consumption in this region. These norms are recalculated and changed every year. Average standards for water disposal, as well as water supply, are disadvantageous to the consumer, since they are calculated for each person. Therefore, in order to save on utility bills, it is worth installing a meter.
All modern enterprises keep records of resources and their consumption. Water consumption is no exception. To calculate the amount of water consumed by the enterprise, to determine the volume of discharged wastewater, there is balance table of water consumption and water disposal(see fig.). Its preparation is necessary to conclude an agreement with the State Unitary Enterprise "Vodokanal". The data in the table show an objective picture of water circulation in the organization and demonstrate exactly how much water is required by a particular enterprise, and how much wastewater is expected to be discharged into the sewer as a result of the life of the object.
What parameters determine the water consumption and water disposal at the enterprise
Water consumption and wastewater disposal at each enterprise is individual, and depends on the following data:- the size of the working staff of the organization;
- use of certain equipment;
- use of special technologies;
- the operating mode of the enterprise;
- the duration of the use of water for industrial processes;
- number of consumers.
We fill in the "Balance of water consumption and wastewater disposal"
Step one. Before compiling the table "BVV" should collect all the initial data. Namely:- name of water consumers;
- numerical value of each water consumer per day with units of measurement;
- water consumption standards for each specific type of water consumer;
- the mode of operation of water consumers per day and per year in separate columns;
- cold water consumption, per day and per year, in separate columns;
- water consumption of hot water, per day and per year by separate columns;
- water disposal per day and per year by separate columns;
- regulatory documents on the basis of which the calculation of standards was made.
Please note that for all initial data, units of measurement should be determined (the number of liters per person, cubic meters, square meters, hours, pieces, etc.).
We fill in the first three columns of the form for the balance of water consumption and wastewater disposal ("serial number", "name of consumers", "amount of water consumption per day"). By the way, there is no specific approved balance sheet, the main thing is that it contains the necessary initial data.
Step two. Populating the table
A set of measures aimed at reducing water consumption will significantly reduce the cost of funds, which will also affect the cost of production, profit by the enterprise It is obvious that compiling a table of the balance of water consumption and wastewater disposal is beneficial for the enterprise itself.
When designing the "Water supply and Sewerage" section, it is necessary to calculate water consumption and water disposal.
SNiP 2.04.01-85 * "INTERNAL WATER PIPELINE AND SEWERAGE OF BUILDINGS" will help us with this.
Document SNiP 2.04.01-85 * is outdated, and you must use the updated edition of SNiP 2.04.01-85 - SP 31.13330.2012.
But the new edition does not explain in any way how to calculate water consumption.
After calculating the water consumption, we will get the following water consumption for all and hot water separately: Secondary water consumption, Hourly water consumption, Daily water consumption. As well as the drainage of waste water into the sewerage system: Secondary water consumption, Hourly water consumption, Daily water consumption.
Let's start calculating:
Let's refer to the first document:
3. DETERMINATION OF DESIGNED WATER FLOWS IN WATER SUPPLY AND SEWERAGE SYSTEMS AND HEAT FOR THE NEEDS OF HOT WATER SUPPLY
3.1. Systems of cold, hot water supply and sewerage must provide water supply and wastewater disposal (flow rate) corresponding to the estimated number of water consumers or installed sanitary devices.
3.2. The second water flow rate, l / s, by water fittings (device), referred to one device, should be determined:
a separate device - according to the mandatory;
various devices serving the same water consumers at the section of the dead-end network - according to the mandatory;
various devices serving different water consumers - according to the formula 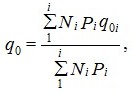 (1)
(1)
where Pi is the probability of action of sanitary devices, determined for each group of water consumers in accordance with clause 3.4.
q0i is the second water consumption (total, hot, cold), l / s, by the water fittings (device), taken in accordance with the mandatory Appendix 3, for each group of water consumers.
Notes:
1. When arranging a ring network, the water flow q0 should be determined for the network as a whole and taken to be the same for all sections.
2. In residential and public buildings and structures for which there is no information on water consumption and technical characteristics sanitary appliances, it is allowed to take:
Determination of the Secondary Consumption
To determine the Secondary water consumption, as a rule, it is sufficient to use Appendices 2 and / or 3 of SNiP 2.04.01-85 *. Less commonly by formula (1).
These applications contain data tables.
Appendix 2: WATER AND WATER FLOW RATE FOR SANITARY APPLIANCES
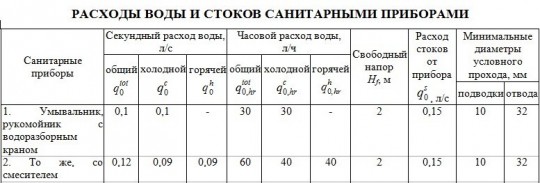
Those. how much water is consumed by 1 sanitary appliance installed in the room.
Or use Appendix 3: WATER CONSUMPTION STANDARDS FOR CONSUMERS
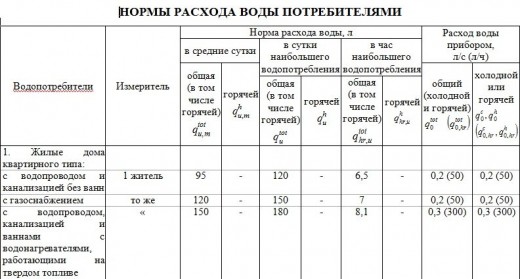
If 10 residents live in the building, 5 employees or the restaurant prepares 300 meals a day. Then we use .
3.3. The maximum second water consumption in the calculated section of the network q (qtot, qh, qc), l / s, should be determined by the formula
where is the second water consumption, the value of which should be determined in accordance with clause;
alpha is the coefficient determined according to the recommended one, depending on the total number of devices N on the calculated network section and the probability of their action P, calculated in accordance with p. In this table. 1 of the recommended one should be guided by P> 0.1 and N of Appendix 4.
With known calculated values of P, N and values q0 = 0.1; 0.14; 0.2; 0.3 l / s to calculate the maximum second water flow, it is allowed to use nomograms 1-4 of the recommended Appendix 4.
Notes: 1. Water consumption at the end sections of the network should be taken as calculated, but not less than the maximum second water consumption by one of the installed sanitary devices.
2. The consumption of water for the technological needs of industrial enterprises should be determined as the sum of the consumption of water by the technological equipment, provided that the operation of the equipment coincides in time.
3. For auxiliary buildings of industrial enterprises, the value of q is allowed to be determined as the sum of water consumption for domestic needs according to formula (2) and shower needs - according to the number of installed shower nets according to mandatory Appendix 2.
3.4. The probability of action of sanitary devices P (Ptot, Ph, Pc) in the network sections should be determined by the formulas:
a) with the same water consumers in the building (s) or structure (structures) without taking into account the change in the U / N ratio
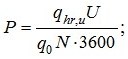 (3)
(3)
b) with different groups of water consumers in a building (buildings) or structures (structures) for various purposes
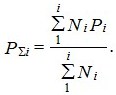 (4)
(4)
Notes:
1. In the absence of data on the number of sanitary appliances in buildings or structures, the value of P is allowed to be determined by formulas (3) and (4), taking N = 0.
2. With several groups of water consumers, for which the periods of the highest water consumption will not coincide in time of day, the probability of device operation for the system as a whole can be calculated using formulas (3) and (4) taking into account the reduction factors determined during the operation of similar systems.
3.5. The maximum second flow rate of wastewater qs, l / s, should be determined:
a) with a total maximum second water flow qtot =
![]() (5)
(5)
b) in other cases.
Determining Hourly Consumption
3.6.
Hourly water consumption by a sanitary appliance 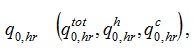 l / h, it should be determined:
l / h, it should be determined:
a) with the same water consumers in a building (buildings) or structure (structures) in accordance with the mandatory Appendix 3;
b) with different water consumers in a building (buildings) or structure (structures) - according to the formula
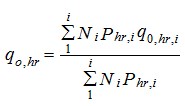 (6)
(6)
Note. In residential and public buildings (structures) for which there is no information on the number and technical characteristics of sanitary appliances, it is allowed to take:
But sanitary appliances are not used all at the same time. Although when advertising in a popular TV series, it is possible that all the toilet bowls in the house go off at the same time. In general, therefore, the probability of using sanitary appliances is calculated
3.7. The likelihood of using sanitary appliances Phr for the system as a whole should be determined by the formula
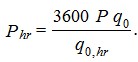 (7)
(7)
3.8. Maximum hourly water consumption ![]() m3 / h, should be determined by the formula:
m3 / h, should be determined by the formula:
![]() (8)
(8)
where is the coefficient determined according to the recommended Appendix 4 depending on the total number of devices N served by the designed system and the probability of their use Phr, calculated in accordance with clause 3.7. In this table. 1 of Recommended Appendix 4 should be followed when Phr> 0.1 and N
Note. For auxiliary buildings of industrial enterprises, the qhr value is allowed to be determined as the sum of water consumption for the use of showers and household and drinking needs, taken according to the mandatory Appendix 3 according to the number of water consumers in the most numerous shift.
3.9. Average hourly water consumption ![]() m3 / h, for the period (day, shift) of the maximum water consumption T, h, should be determined by the formula:
m3 / h, for the period (day, shift) of the maximum water consumption T, h, should be determined by the formula:
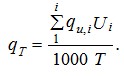 (9)
(9)
3.10. When designing direct water intake from pipelines of a heating network for the needs of hot water supply, the average temperature of hot water in the risers should be maintained equal to 65 ° C, and the rates of hot water consumption should be taken in accordance with the mandatory Appendix 3 with a coefficient of 0.85, while the total amount of consumed water should not be changed ...
3.11. The maximum hourly flow rate of wastewater should be taken equal to the estimated flow rate determined in accordance with paragraph 3.8.
3.12. The daily water consumption should be determined by summing the water consumption by all consumers, taking into account the water consumption for irrigation. The daily consumption of wastewater must be taken equal to the water consumption without taking into account the water consumption for irrigation.
3.13. Heat flow kW, for the period (day, shift) of the maximum water consumption for the needs of hot water supply (taking into account heat loss) should be calculated by the formulas:
a) for an average hour
![]() (10)
(10)
b) during the hour of maximum consumption
I looked with a fresh eye and realized that at first glance it all seemed very complicated and incomprehensible. But it is worth doing the calculation once and everything falls into place.
I think for clarity, we need to make an example of the calculation.





