High quality stainless steel hardware, mainly made of steel grades A2 (analogue of steel 12X18H9 in accordance with GOST or AISI 304 in the USA) and A4 (analogue of steel 03X17H14M2 in accordance with GOST or AISI 316 in the USA) are most often generalized into one class of metal products.
Steel grade A2 - austenitic stainless steel. Corrosion resistant, non-magnetic and non-toxic. The stainless steel hardware made from it is recommended for use in general construction works.
Steel grade A4 - austenitic acid-resistant steel. It differs from the A2 steel grade by the addition of 2-3% molybdenum, which significantly increases its ability to resist corrosion and acids. A4 steel is completely non-magnetic. Fastener A4 is recommended for use in shipbuilding, food industry and is suitable for use in acids and environments containing chlorine.
Steel grades A2 and A4 have a number of important characteristics:
- High degree of resistance to corrosion;
- Strength;
- Hygiene;
- Long service life;
- Aesthetically attractive and presentable appearance;
- Resistance to high and low temperatures from -200 C to +600 C.
They are used in various industries:
- Aviation;
- Building;
- Mechanical engineering;
- Food industry:
- Furniture manufacture;
- Shipbuilding;
- Automotive;
- Khimprom;
- Manufacturing of medical equipment, etc.
Stainless hardware has the following strength classes:
- 50 - soft;
- 70 - riveted;
- 80 - high strength.
Strength class in stainless hardware is indicated by a dash after the steel grade. For example: DIN 931 M12x40 A4-80 where
A4 - steel grade;
80 - strength class.
From the OPM warehouse you can purchase stainless steel hardware from A2, A4 steel grades:
Nuts:
Wing nut DIN 315 A.F
Low nut DIN 439 analogue of GOST 5916, 5929
Hex nut DIN 934 analogue of GOST 5915, 5927
Low self-locking nut DIN 985
Cap nut DIN 1587 analogue of GOST 11860
Self-tapping screw with countersunk head and cross recess DIN 7982 analogue of GOST 1145
Screw universal countersunk head and Pz slot
Rod and studs including,
Hairpin with a screwed end 1.25 d long analogue of GOST 22034, 22035
Threaded rod 1-2 meters DIN 976 (former DIN 975)
Other:
Traction rivets DIN 7337
Pins DIN 7
Cotter pin DIN 94 analogue of GOST 397
When selecting stainless steel hardware, use the table "Mechanical properties of connecting elements: austenitic steel grades"
table is being edited
Since chromium-nickel steels cannot be hardened, an increased yield strength is achieved only by work hardening under a cold forming press. Therefore, when selecting set screws, use the table


The scope of stainless steel fasteners is very extensive. To technological installations of the chemical, pharmaceutical, food industries, increased requirements are imposed on work under conditions of exposure to chemically aggressive substances, hygiene, durability. Many elements of these machines and mechanisms are made of high-alloy, corrosion-resistant stainless steels... Of course, these elements also include a variety of stainless steel fasteners.
Types of stainless steel fasteners
Today, in the trade network and from representatives of manufacturing plants, you can choose stainless steel hardware of any kind. Depending on your needs, the following types of stainless steel fasteners are available:
- with hex head, full and partial threads;
- swing bolts;
- eye bolts;
- mounting, with semicircular, countersunk and hexagonal heads, with straight, cross-shaped recesses and hexagonal holes;
- flat washers, oblique, with a rectangular hole and Grover's washers;
- retaining rings and washers;
- cylindrical and conical pins;
- single- and seven-strand cables;
- short link chains;
- with a semicircular, countersunk and hexagonal head, with a straight and cross recess.
The range of stainless steel hardware allows you to select the required type of fastener, depending on the specific conditions of its operation.



Fasteners are made of stainless steel A2, A4 or their domestic counterparts - 12Х18Н9Т, 10Х17Н14М2Т. Stainless steel A2 is not subject to hardening, retains its properties up to a temperature of -200 ° C. Hardware made of this stainless steel is easily welded without increasing fragility. A2 stainless steel hardware and fasteners are not used in acidic and chlorine-containing environments. Steel A4 differs from A2 by a 2-3% increase in molybdenum content, which makes it more resistant to acids. The main areas of application of A4 steel are shipbuilding, the production of hardware and products for rigging.
Benefits of stainless steel fasteners
The advantages of stainless steel hardware include the following:
- non-toxic, which makes it possible to use it in devices for the food and pharmaceutical industries, as well as for the production of medical equipment and equipment for cooking;
- non-magnetic, which allows the use of stainless steel fasteners in instrument making;
- preservation of strength characteristics in a wide temperature range;
- the ability to manufacture interior elements that fit into the High-tech style.
All this makes stainless steel hardware in demand in the fasteners market.
The remarkable properties of stainless steel have been known to man for a long time. Stainless steel is resistant to corrosive processes and is unpretentious in operation. When you need to create a reliable connection that is resistant to aggressive factors, the best option would be to use stainless steel fasteners. The material of the bolts, with their inherent characteristics, is paramount for a strong fastening.
Applications for stainless bolts
A4 stainless bolts are used in many areas of mechanical engineering, construction work, as well as in the production of household appliances. In places where welding fastening cannot be applied, A4 stainless bolt becomes in demand, showing anti-corrosion characteristics and strength. The stainless steel mount meets modern standards and requirements.
Characteristics of the A4 bolt
The A4 stainless steel bolt is non-magnetic, strong and durable in operation. This fastener is well exposed to mechanical processing and thermal manipulation. Temperature fluctuations from the lowest to the highest do not change the properties and characteristics of the A4 stainless bolt. The fastener can also be used in environments with exposure to acids and corrosive liquids, which cannot affect the tightness of the connection of the parts. A4 steel is similar to A2 steel, but due to the addition of up to 2-3 percent molybdenum to its composition, it provides higher performance characteristics. Although the price of A4 stainless steel bolts will be higher than that of conventional carbon steel, their durability will pay off over time.
Features of production
The production of A4 stainless steel bolts is carried out from an alloy consisting of low carbon steel, chromium, nickel and three percent molybdenum. These components give the products high performance parameters, which are manifested in anti-corrosion resistance, non-susceptibility to the influence of thermal and mechanical influences. Molybdenum additive allows you to use stainless bolts in especially aggressive environments containing acids and chlorides: in the chemical industry, at shipyards, in swimming pools.
Characteristics of steel 12x18n10t
Density | 7630 kg / cubic meter |
Appointment | parts working up to 600 ° C. Welded apparatus and vessels operating in dilute solutions of nitric, acetic, phosphoric acids, solutions of alkalis and salts and other parts operating under pressure at temperatures from -196 to +600 ° C, and in the presence of aggressive media up to +350 ° C; austenitic steel |
Elastic modulus | |
Shear modulus | |
Weldability | Weldable without limits |
Forging temperature | Beginning 1200, end 850. Sections up to 350 mm are cooled in air. |
Chemical composition | Silicon: 0.8, Manganese: 2.0, Copper: 0.30, Nickel: 9.0-11.0, Sulfur: 0.020, Carbon: 0.12, Phosphorus: 0.035, Chromium: 17.0-19.0, Titanium: 0.6-0.8, |
A2, A4 - Characteristics of stainless steel fasteners
Stainless steels A2, A4: structure, mechanical properties, chemical composition... Fasteners made of steel A2, A4 (stainless bolts, screws, nuts, washers, pins, etc.): mechanical properties, values of tightening torques and pre-tightening forces.
Austenitic steels contain 15-26% chromium and 5-25% nickel, which increase corrosion resistance and are practically non-magnetic.
It is the austenitic chromium-nickel steels that exhibit a particularly good combination of machinability, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. This group of steels is most widely used in industry and in the production of fasteners.
Steels of the austenitic group are designated by the initial letter "A" with an additional number that indicates the chemical composition and applicability within this group:
Austenitic structure
Steel group | Material number | Short designation | AISI number |
X 5 CrNi 18-10 / X 4 CrNi 18-12 | AISI 304 / AISI 305 |
||
X 6 CrNiTi 18-10 | |||
X 5 CrNiMo 18-10 / X 2 CrNiMo 18-10 | AISI 316 / AISI 316 L |
||
X 6 CrNiMoTi 17-12-2 |
Steel A2 (AISI 304 = 1.4301 = 08Х18Н10)- non-toxic, non-magnetic, non-hardened, corrosion-resistant steel. Easily weldable and does not become brittle. Can exhibit magnetic properties as a result of machining (washers and some types of screws). This is the most common group of stainless steels. The closest analogues are 08Х18Н10 GOST 5632, AISI 304 and AISI 304L (with a reduced carbon content).
Fasteners and products made of A2 steel are suitable for use in general construction work (for example, when installing ventilated facades, stained-glass structures made of aluminum), in the manufacture of fences, pumping equipment, instrumentation from stainless steel. steel for oil and gas, food, chemical industries, shipbuilding. Retains strength properties when heated up to 425oС, and at low temperatures up to -200oС.
Steel A4 (AISI 316 = 1.4401 = 10Х17Н13М2)- differs from steel A2 by the addition of 2-3% molybdenum. This greatly increases its ability to resist corrosion and acid attack. A4 steel has higher anti-magnetic characteristics and is absolutely non-magnetic. The closest analogues are 10Х17Н13М12 GOST 5632, AISI 316 and AISI 316L (with low carbon content).
Fasteners and rigging made of A4 steel are recommended for use in shipbuilding. Fasteners and products made of A4 steel are suitable for use in acids and chlorine-containing environments (such as swimming pools and salt water). It can be used at temperatures from -60 to 450 ° C.
Strength classes
Everything austenitic steels(from "A1" to "A5") are subdivided into three strength classes, regardless of the grade. Steels in the annealed state have the lowest strength (strength class 50).
Since austenitic steels are not hardened by hardening, they have the greatest strength in the cold-worked state (strength classes 70 and 80). The most widely used fasteners are A2-70 and A4-80 steels.
Basic mechanical properties of austenitic steels:
ASTM type (AISI) | |||||
Specific gravity (g / cm) | |||||
Mechanical properties at room temperature (20 ° C) |
|||||
Brinell hardness - HB | Annealed | ||||
Rockwell hardness - HRB / HRC | |||||
Tensile strength, N / mm 2 | |||||
Tensile strength, N / mm2 | |||||
Relative extension | |||||
Impact strength | KCUL (J / cm 2) | ||||
KVL (J / cm 2) | |||||
Mechanical properties when heated |
|||||
Tensile yield strength, N / mm2 | |||||
Basic mechanical properties of bolts made of steel A2, A4different strength classes:
Chemical composition of stainless steel:
Steel grade | Group | Chemical composition (wt%) 1) Extract from DIN EN ISO 3506 |
|||||||||
Note |
|||||||||||
Austenitic | 0,15 | 1,75 | |||||||||
16 | 10,5 | ||||||||||
16 | 10,5 | ||||||||||
1) Maximum values unless otherwise specified.
2) Sulfur can be replaced with selenium.
3) If the mass fraction of nickel is below 8%, then the mass fraction of manganese must be at least 5%.
4) There is no minimum limit for the copper mass fraction if the nickel mass fraction is more than 8%.
5) Molybdenum is allowed at the discretion of the manufacturer. If for certain applications it is necessary to limit the molybdenum content, this should be indicated by the customer.
6) Molybdenum is also permitted at the discretion of the manufacturer.
7) If the mass fraction of chromium is below 17%, then the mass fraction of nickel must be at least 12%.
8) In austenitic steel with a maximum carbon mass fraction of 0.03%, the nitrogen must be maximum 0.22%
9) For stabilization, titanium ≤ 5xC must be present up to a maximum of 0.8% and be labeled according to this table or niobium and / or tantalum ≤ 10xC up to a maximum of 1% and be labeled according to this table.
Austenitic chromium-nickel steels show a particularly good combination of machinability, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Therefore, they are recommended for many applications and are the most significant group of stainless steels. The most important property of this group of steels is high corrosion resistance, which increases with an increase in the content of alloying, especially chromium and molybdenum.
Stainless steel is the most widely used material for food production, storage and transportation equipment. This is due to the high requirements that it must meet in terms of hygiene, toxicity, etc.
Wine production environments are highly corrosive to carbon steels. The aggressiveness of various wines is determined by the content of sugars, organic acids, sulfurous anhydride and alcohol. These figures vary significantly depending on the type of wine. Thus, table (dry) wines do not contain sugars, but only 9-14% vol. alcohol, fortified wines contain 8 - 10% vol. Sugars and 16 - 20% vol. alcohol, sweet dessert wines - 8-20% vol. Sugars and more than 13% vol. alcohol, semi-sweet table wines - 3 - 7% vol. Sugars and 7 - 12% vol. alcohol. The mass concentration of titratable acids is in the required GOST range (3-8 g / dm3). Sulfurous anhydride is traditionally used in wort clarification. Permissible concentration (MPC) of sulfurous anhydride in wines, as a rule, is not more than 150 - 400 mg / l.
In alcohol and alcoholic beverage industries, technological media are corrosive. They may contain unfermented sugar, organic acids, esters, fusel oils, aldehydes, etc. These media include mash (grain, molasses, cane), rectified alcohol, raw alcohol, vinasse, as well as vodka, various liqueurs , tinctures and low alcohol drinks.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ALLOYS AND THEIR APPLICATION
The characteristics of various stainless steel alloys are given in table. 1 and 2.
Some Russian suppliers persistently convince consumers that pipes made of AISI 430 (12X17) steel can also be used in pipelines for the food industry. This is incorrect, since clause 4 of DIN 11850 ("Materials") unambiguously indicates that in the food industry only the following steels can be used as standard: AISI 304 (1.4301), AISI 304L (1.4307), AISI 316L (1.4404).
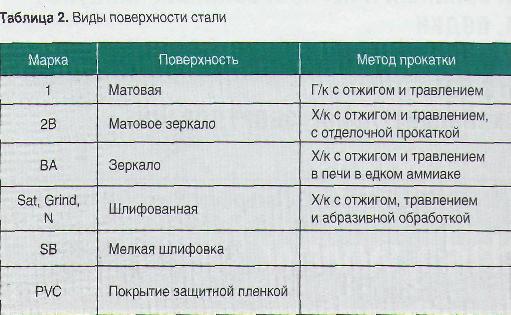
This group of stainless steels is the most widely used and includes grades 304 and 316. These materials are ideal for use in food processing, milk, wine and distillery, brewing, pharmaceutical, chemical and petrochemical industries. 304 stainless steels contain about 18% chromium and 10% nickel and exhibit excellent corrosion resistance. Where particularly high corrosion resistance is required under extreme conditions, especially where chlorides are present, grade 316 steels are used containing about 17% chromium, 12% nickel and 2.2% molybdenum. Steel 12X18H10T is acid-resistant, not subject to intercrystalline corrosion, heat-resistant up to 600 ° C. It is used to make equipment for milk processing, cans, flasks, fermentation vats, barrels, storage equipment for wine-making and distillery enterprises, as well as utensils for cooking and equipment for kitchens and canneries.
Unlike other stainless steels, austenitic grades are non-magnetic, and as a result, magnetic particles do not adhere to the walls of the system, which could otherwise cause clogging.
Ferritic stainless steels(much softer than martensitic, due to the low carbon content; also have magnetic properties, denoted by the initial letter F).
Ferritic stainless steels are less corrosion resistant than 304 and 316 austenitic grades and are used where requirements are less demanding. Ferritic steels contain 11.5-16.5% chromium and less than 0.5% nickel. Steels in this group are magnetic and will cause adhesion of magnetic particles, which can lead to contamination problems. Ferritic steels are unsuitable for the manufacture of drainage products.
Martensitic stainless steels(much harder than austenitic steels and can be magnetic; more susceptible to corrosion, indicated by an initial C).
Martensitic steels are magnetic and are characterized by the highest strength in the group of stainless steels, while at the same time they have the least resistance to corrosion. They can be heat-hardened and are mainly used for the manufacture of knife tools.
The types of steels of the most common - austenitic - group are indicated by an additional number, which indicates the chemical composition and applicability within this group:
... A1- are used, as a rule, in mechanical and movable assemblies. Due to the high sulfur content, steels of this type are less able to resist corrosion than other types;
... A2- non-toxic, non-magnetic, non-hardening, corrosion-resistant steels. Easily weldable and non-brittle. May show magnetic properties as a result of machining (washers and some types of screws). This is the most common group of stainless steels. Fasteners and products made of A2 steels are not suitable for use in acids and environments containing chlorine (for example, in swimming pools and salt water). They are suitable for temperatures down to -200 ° C. The closest analogues are AISI 304 and AISI 304L with even lower carbon content;
... A3- similar in properties to A2 steels and additionally stabilized with titanium, niobium or tantalum. This increases their resistance to corrosion when high temperatures;
... A4- similar to steel A2, but with the addition of 2 - 3% molybdenum. This makes them much more capable of resisting corrosion and acid attack. Fasteners and rigging from A4 are recommended for use in shipbuilding. Suitable for temperatures down to -60 ° C. The closest analogues are AISI 316 and AISI 316L with low carbon content;
... A5- has the properties of A4 steels and is additionally stabilized with titanium, niobium or tantalum, like A3, but with a different content of alloying additives. It also increases its resistance to high temperatures.

The choice of stainless steel grade for each application is very important. It should be remembered that even stainless steels of grades 316 are not protected from all types of chemical attack, for example from use with reducing solutions such as hydrochloric and oxalic acids, especially in a concentrated and / or heated state.
"Distillery and winemaking" No. 10 (106), October 2008
A. S. Boguslavsky





