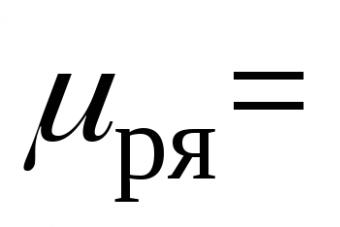In the process of moving charges inside a closed chain, a source of current is performed. It can be useful and complete. In the first case, the current source moves charges in the external circuit, while doing work, and in the second case, the charges move throughout the chain. In this process, the efficiency of the current source defined as the ratio of the external and complete resistance of the chain is of great importance. With the equality of the internal resistance of the source and external load resistance, half the total power will be lost in the source itself, and the other half is highlighted on the load. In this case, the efficiency will be 0.5 or 50%.
Efficiency electric chain
The coefficient under consideration is primarily associated with physical quantities characterizing the transformation rate or transmission of electricity. Among them, in the first place is the power measured in watts. To determine it, there are several formulas: p \u003d u x i \u003d u2 / r \u003d i2 x r.
In electrical circuits, there may be a different value of the voltage and the value of the charge, respectively, the work performed is also different in each case. Very often there is a need to evaluate, at what speed is transmitted or transformed with electricity. This speed is an electrical power corresponding to the work performed for a certain time unit. In the formula formula, this parameter will look as follows: p \u003d a / Δt. Consequently, the work is displayed as a product of power and time: a \u003d p ∙ Δt. As a unit of measurement of work is used.
In order to determine how efficiently any device, the electrical circuit machine or the other similar system, the efficiency is used in terms of power and work efficiency - useful action coefficient. This value is defined as the ratio of useful energy consumed, to the total amount of energy entered into the system. The efficiency is indicated by the symbol η, and mathematically determined in the formula form: η \u003d A / Q x 100% \u003d [J] / [J] x 100% \u003d [%], in which A is the work performed by the consumer, Q is the energy given by the source . In accordance with the law of energy conservation, the efficiency of the efficiency is always equal to or below one. This means that useful work cannot exceed the amount of energy spent on its commission.

Thus, power loss is determined in any system or device, as well as the degree of their utility. For example, in power loss conduirers, it is formed when the electric current is partially turning into thermal energy. The number of these losses depends on the resistance of the conductor, they are not an integral part of the useful work.
There is a difference expressed by the formula Δq \u003d A-Q, clearly reflecting power loss. It looks very well a dependence between the growth of power losses and the conductor resistance. The most striking example is the incandescent lamp, the efficiency of which does not exceed 15%. The remaining 85% of power turn into thermal, that is, infrared radiation.
What is the CPD source of the current
The considered efficiency of the entire electrical circuit, makes it possible to better understand the physical essence of the efficiency of the current source, the formula of which also consists of various values.

In the process of moving electrical charges along a closed electrical circuit, a source of current is performed a specific work, which differs as useful and complete. During the fulfillment of useful work, the current source moves charges in the external chain. With complete work, charges, under the action of the current source, move along the entire chain.
As formulas, they are displayed as follows:
- Useful work - Apolesis \u003d QU \u003d IUT \u003d I2RT.
- Full work - appointment \u003d qε \u003d iεt \u003d i2 (r + r) t.
Based on this, you can withdraw the formula for the useful and complete power source power:
- Useful power - RPPLES \u003d Apolez / T \u003d IU \u003d I2R.
- Full power - Rpoven \u003d Appeaps / T \u003d iε \u003d i2 (R + R).
As a result, the CPD formula of the current source acquires the following form:
- η \u003d Apolesis / Appeaps \u003d RPLES / RPL \u003d U / ε \u003d R / (R + R).
Maximum useful power is achieved with a certain value of the resistance of the outer chain, depending on the characteristics of the current source and load. However, attention should be paid to incompatibility of maximum useful power and maximum efficiency.
Investigation of power and efficiency source
The efficiency of the current source depends on many factors that should be considered in a certain sequence.

To determine, in accordance with the Ohm's law, there is the following equation: I \u003d E / (R + R), in which E is the electromotive force of the current source, and R is its internal resistance. These are constant values \u200b\u200bthat do not depend on variable resistance R. With their help, it is possible to determine the useful power consumed by an electrical chain:
- W1 \u003d i x U \u003d I2 x R. Here R is the resistance of the power consumer, I - current in the chain defined by the previous equation.
Thus, the power value using finite variables will be displayed in the following form: W1 \u003d (E2 x R) / (R + R).
Since it is an intermediate variable, then in this case the function W1 (R) can be analyzed to the extremum. To this end, it is necessary to determine the value of R, in which the value of the first derivative of the useful power associated with variable resistance (R) will be zero: DW1 / DR \u003d E2 X [(R + R) 2 - 2 x R x (R + R) ] \u003d E2 x (Ri + R) x (R + R - 2 x R) \u003d E2 (R - R) \u003d 0 (R + R) 4 (R + R) 4 (R + R) 3
From this formula, it can be concluded that the value of the derivative can be zero only under one condition: the resistance of the electricity receiver (R) from the current source must reach the internal resistance of the source itself (R \u003d\u003e R). Under these conditions, the value of the efficiency of η will be determined as the ratio of the useful and complete power of the current source - W1 / W2. Since at the maximum point of useful power, the resistance of the consumer energy of the current source will be the same as the internal resistance of the source itself, in this case the efficiency will be 0.5 or 50%.
Tasks for current and efficiency
8.5. Thermal effect of current
8.5.4. Efficiency electrical appliances
Electrical appliances are designed to transform electrical energy to other types of energy (thermal, mechanical, etc.). When converting energy, part of it dissipates due to the imperfection of the design of the instruments.
Heating a physical object or to change it aggregate state (for example, for melting substance, a soldering iron is sometimes used), determined by the formula
where q is the heat transmitted by the body; E electric - electrical energy generated by the device, E electr \u003d Pt; P - power of an electrical device; T - the time of the device.
Efficiency of an electrical device intended for changes in mechanical energy A physical object (for example, a lifting mechanism with an electric drive can sometimes use a lifting mechanism for a certain height), determined by the formula
η \u003d Δ W fur E electric ⋅ 100%,
where ΔW fur is a change in the mechanical energy of the body; E electric - electrical energy generated by the device, E electr \u003d Pt; P - power of an electrical device; T - the time of the device.
Efficiency of an electrical device intended for work performed Over any physical object (for example, the electric motor is sometimes used to move the cargo along the horizontal surface), determined by the formula
η \u003d a e electr ⋅ 100%,
where a is the work performed above the body; E electric - electrical energy generated by the device, E electr \u003d Pt; P - power of an electrical device; T - the time of the device.
Example 18. With the help of a heater with an efficiency of 80% included in the network, water is heated with a specific heat capacity of 4.2 J / (g ⋅ K). For the hour of work, the heater boiled 8.4 kg of water taken at 20 ° C. Determine the power of the heater.
Decision . The efficiency of the heater is determined by the formula
η \u003d q e electr ⋅ 100%
where q is the amount of heat required to heat the specified amount of water; E electrical energy generated by heater.
The amount of heat required to heat the water to the boiling point is determined by the formula
Q \u003d mc dd (T kip - T 0),
where m is the mass of water, m \u003d 8.4 kg; with ud - specific heat capacity of water, with dd \u003d 4.2 J / (g ⋅ K); T Kip - water boiling point, T kip \u003d 100 ° C; T 0 - the initial temperature of the water, T 0 \u003d 20 ° C.
The electrical energy generated by the heater is determined by the work
E electr \u003d P electric t,
where P electrical power of the heater (the desired value); T - the operating time of the heater.
We write the formula for the efficiency of the heater, taking into account the expressions that determine Q and E electric:
η \u003d m c ud (T kip - T 0) P electric t ⋅ 100%
and express the desired value:
P Electric \u003d 100 m C d (T Kip - T 0) η T.
Calculate:
P electr \u003d 100 ⋅ 8.4 ⋅ 4.2 ⋅ 10 3 (100 - 20) 80 ⋅ 3600 \u003d 0.98 ⋅ 10 3 W \u003d 0.98 kW.
The heater used to boil water has a power of 0.98 kW.
Laboratory work
Purpose: purposeful learning of search activity, actualization of the personal meaning of students to study the topic, creating conditions for the development of communication skills and joint activities.
Tasks:
Educational: experimental work bydetermining the efficiency of electrical appliances on the example of an electric kettle,the formation of the skill to establish the connection between the elements of the content of the previously studied material and the new one.
Developing: development of mental skills, improving the skills to formulate personal - significant goals, promote the development of research and creative skills.
Educational: Improving the ability to work in a pair, to form the ability to self-analysis.
Type of lesson : Lesson - Workshop (2 hours)
Equipment
During the classes
Organizing time
Safety Instructions when working with electrical measuring devices.
Formulation of the problem.
Calculate the perfect electric shock work
Calculate the amount of heat obtained by water and equal useful work,
determine on experienceEfficiency of electrical appliances on the example of an electric kettle;
Performing work, according to methodical recommendations.
1. Consider the electric kettle. According to passport data, determine the electrical power of the electrical appliance P.
2. Pour into the kettle water with a volume V equal to 1 l (1 kg)
3. Measure using the thermometer the initial water temperature T 1 .
4. Turn on the kettle into the electrical network and heat the water to boil.
5. Determine the water boiling point T 2 .
6. Note the time the time between which the water Δŧ was heated during which
All measurements perform in si.
7. Using measurement data, calculate:
el.Toka \u003d P ∙ Δt
narr. \u003d cm (t 2 - T. 1 )
8. Calculate the efficiency of the electric kettle by the formula
η = =
9. Measurement and computing results to the table
P, T.V, M. 3
t. 1 , 0 FROM
ΔT, S.
t. 2 , 0 FROM
A. el.Toka J.
Q. narr. J.
ŋ,%
Control questions:
Why is the electric kettle spiral made from the conductor of a large cross section? Give a debacious answer.
Give examples of other electrical appliances in which the heating element is a spiral. What do these devices differ from each other?
Welder Why, during electric welding, more heat is allocated precisely in the junction of welded slices? (When passing the current of the high force through the metallic parts in contact with the small plane, the maximum resistance to the current current turns out and, therefore, the maximum amount of heat is distinguished).
Auto Mechanic Why low-power devices are disadvantageous? Why when using such devices is inevitable energy overrun?( Due to the increase in water heating time increases losses by convection, thermal conductivity, radiation)
Output.
5. Homework: Prepare a report, repeat the law of Joule - Lenza.
Laboratory Performance Report
"Determining the efficiency of an electric kettle."
Purpose of work: learn experimentaldetermine the efficiency of electrical appliances using an example of an electric kettle.
Equipment : Electric kettle, thermometer, clock with a second arrow.
Progress:
1. Reviewed the electric kettle. Passport data determined the electrical power of the electrical appliance P.
2. Poured into the kettle water volume V equal to 1 l (1 kg)
3. I measured the initial water temperature with the thermometer T 1 .
4. Included the kettle into the electrical network and heated water to a boil.
5. Determined the water boiling point T 2 .
6. I noticed the time interval for which water Δŧ was heated during which
7. Using measurement data, calculated:
a) electric current operation, knowing the power of the kettle P and the water heating time Δt, according to the formula A el.Toka \u003d P ∙ Δt
b) the amount of warmth obtained by water and equal useful work, q narr. \u003d cm (t 2 - T. 1 )
8. Calculated the efficiency of the electric kettle by the formula
η = =
9. The results of measurements and calculations listed in the table
P, T.V, M. 3
t. 1 , 0 FROM
ΔT, S.
t. 2 , 0 FROM
A. el.Toka J.
Q. narr. J.
ŋ,%
Answers to check questions :
Conclusion about the work done:
As you know, such mechanisms have not yet been created at the moment, which would have turned over one type of energy to the other. In the process of operation, any manual device consumes part of the energy to the resistance of the strength or water dissipates it into the environment. The same thing happens in a closed electrocups. When the charges proceed through the conductors, the resistance of the full and useful load of the operation of electricity is carried out. To compare their ratios, it will be necessary to produce a usefulness coefficient (efficiency).
What is the calculation of the efficiency
The efficiency of the electrical circuit is the ratio of useful heat to full.
For clarity, we give an example. When the engine efficiency is possible, it is possible to determine if its main function of operation costs consumed electricity. That is, its calculation will give a clear picture, how well the device converts the resulting energy.
Note! As a rule, the efficiency does not matter, but is a percentage ratio or numeric equivalent from 0 to 1.
The efficiency is found according to the general formula for calculating, for all devices as a whole. But in order to get its result in the electrical circuit, first it will be necessary to find the power of electricity.
Current location in full chain
In physics, it is known that any current generator has its own resistance, which is still called internal power. In addition, the source of electricity also has its strength.
We give the values \u200b\u200bto each chain element:
- resistance - R;
- current strength - e;

So, to find the strength of the current, the designation of which will be - i, and the voltage on the resistor - u, it will take time - t, with the passage of charge Q \u003d lt.
Due to the fact that the power of electricity is constant, the operation of the generator is entirely transformed into the heat allocated on R and R. Such a number can be calculated by the law of Joule-Lenza:
Q \u003d i2 + i2 rt \u003d i2 (R + R) T.
Then the right parts of the formula are equal:
Eit \u003d i2 (R + R) T.
By drawing a reduction, it turns out the calculation:
By producing a permutation with the formula, as a result, it turns out:
This final value will be an electrical force in this device.
While making a preliminary calculation, now you can define the efficiency.
Calculation of the efficiency of the electrical circuit
The power obtained from the current source is called consumed, its definition is written - P1. If this physical value moves from the generator to the full chain, it is considered useful and recorded - P2.
To determine the CPD of the chain, it is necessary to recall the law of conservation of energy. In accordance with it, the power of the R2 receiver will always be less than the power consumed P1. This is explained by the fact that in the process of work in the receiver always occurs inevitable waste of convertible energy, which is spent on the heating of the wires, their shell, vortex currents, etc.
To find an estimate of the properties of the conversion of energy, the efficiency is necessary, which will be equal to the ratio of the power P2 and P1.
So, knowing all the values \u200b\u200bof the indicators constituting electrocups, we find it useful and complete work:
- And useful. \u003d QU \u003d IUT \u003d I2RT;
- And complete \u003d Qe \u003d IET \u003d i2 (R + R) T.
In accordance with these values, we will find the power source power:
- P2 \u003d and useful / t \u003d iu \u003d i2 r;
- P1 \u003d and complete / t \u003d ie \u003d i2 (R + R).
By producing all actions, we get the Formula of the CPD:
n \u003d and useful / and complete \u003d P2 / P1 \u003d U / E \u003d R / (R + R).
This formula, it turns out that R is above infinity, and n above 1, but with all this current in the chain remains low, and its useful power is small.
Everyone wants to find an efficiency efficiency. To do this, it is necessary to find the conditions under which P2 will be maximum. The optimal values \u200b\u200bwill be:
- P2 \u003d i2 r \u003d (E / R + R) 2 R;
- dP2 / DR \u003d (E2 (R + R) 2 - 2 (R + R) E2 R) / (R + R) 4 \u003d 0;
- E2 ((R + R) -2R) \u003d 0.
In this expression, E and (R + R) are not equal to 0, therefore, it is equal to the expression in brackets, that is, (R \u003d R). Then it turns out that power has the maximum value, and the efficiency coefficient \u003d 50%.
As can be seen, it is possible to find the efficiency of the electrical circuit independently without resorting to the services of a specialist. The main thing is to comply with the sequence in the calculations and not go beyond the formulas given.
Video
It is known that the eternal engine is impossible. This is due to the fact that for any mechanism, the approval is true: complete work performed with the help of this mechanism (including the heating of the mechanism and the environment, to overcome the friction force) is always more useful work.
For example, more than half of the operation of the internal combustion engine takes place isted spent on the heating of the components of the engine; Some amount of heat carry out exhaust gases.
It is often necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of the mechanism, the feasibility of its use. Therefore, in order to calculate what part of the perfect work is wasted and which is a part with benefit, a special physical value is introduced, which shows the effectiveness of the mechanism.
This value is called the efficiency of the mechanism
The efficiency of the mechanism is equal to the ratio of useful work to complete work. Obviously, the efficiency is always less than one. This value is often expressed as a percentage. Usually it is denoted by the Greek letter η ("this") is read. An abbreviated efficiency is recorded by the efficiency.
η \u003d (A_P / A_Poles) * 100%,
where η kpd, a_tile work, and_ is a useful job.
Among the engines the largest efficiency has an electric motor (up to 98%). The efficiency of the internal combustion engines is 20% - 40%, the steam turbine is about 30%.
Note that for increase the efficiency of the mechanism Often try to reduce the strength of friction. This can be done using various lubricants or ball bearings in which the friction of sliding is replaced by friction of rolling.
Examples of calculating the efficiency
Consider an example. A cyclist weighing 55 kg rose by a bike weighing 5 kg per hill, whose height is 10 m, while making the work of 8 kJ. Find the efficiency of the bike. Friction of rolling wheels about the road do not take into account.
Decision. Find a total mass of bike and cyclist:
m \u003d 55 kg + 5 kg \u003d 60 kg
We will find their total weight:
P \u003d Mg \u003d 60 kg * 10 N / kg \u003d 600 N
Find the work performed on the rise of the bike and the cyclist:
APLESS \u003d PS \u003d 600 H * 10 m \u003d 6 kJ
Find the KPD bike:
A_Faple / A_Poles * 100% \u003d 6 kJ / 8 kJ * 100% \u003d 75%
Answer: The KPD of the bicycle is 75%.
Consider another example. At the end of the lever, the body m is suspended. To another shoulder, the force f is attached downward, and its end is lowered on h. Find how much the body rises if the efficiency of the lever is equal to η%.
Decision. Find the work performed by the force F:
η% of this work is made to raise the body mass M. Therefore, FHη / 100 is spent on the lifting of the body. Since the body weight is equal to Mg, the body rose to the height FHη / 100 / Mg.