pace. From these considerations, it follows that there is an optimal ratio between equity and borrowed capital, corresponding to the minimum average cost of financing. This optimal capital structure depends on industry characteristics, special situations within the enterprise and capital market conditions. The most general recommendation is that the share of borrowed capital should not exceed the company's own funds. Upon reaching the optimal structure, in order to be able to use additional sources of borrowed capital without violating the structure of sources, it is necessary to increase equity capital in the same amount.
5.2. Financial planning at the enterprise
Planning, as one of the most important functions of production management, is a process of developing, building a plan, a method of future actions, determining directions for the development of a business entity. In the planning process, drafts of the desired state of the economic entity in possible (expected) conditions are developed, the content and sequence of steps leading to the intended goal are worked out, and final results are established.
The main essential features of planning are:
- focus on the future;
- determination of deadlines;
- development of a system of indicators that should be
achieved as a result of their implementation and implementation. The purpose of planning is to create guidelines for future activities.
At enterprises, depending on the control object, a planning object and, accordingly, an object-oriented planning area are distinguished.
As a rule, enterprises distinguish between:
- technical and economic planning;
- work planning and salary;
- production planning;
- financial planning.
financial planning stands out among these areas of planning:
- as an element of enterprise financial management;
- as a subsystem of economic and business planning in the enterprise.
Currently, there are two main classifications of types of financial planning:
1) according to the time period for which the plans are drawn up:
- short-term (up to 1 year, month, quarter);
- medium term for 1 year;
- long-term for a period of more than 1 year.
Based on this classification, the needs are linked with the sources and tools for raising funds to cover them:
- for the short term - accounts payable;
- for the medium term - a bank loan;
- for a long-term - investment loan, bonded loan, issue of shares;
2) according to the tasks, the solution of which should be provided:
- strategic (perspective);
current;
Operational.
The systemic nature of financial planning in an enterprise is ensured by the presence and interrelation of the following elements:
- purpose of financial planning;
- subjects of financial planning;
- the subject of financial planning;
- objects of financial planning;
- principles of financial planning;
- methods of financial planning;
- information support for planning;
- forms of financial planning;
- results of financial planning;
- evaluation of the effectiveness of financial planning at the enterprise. Therefore, further financial planning is proposed to be considered in
section of each element of the system.
Financial planning in an enterprise begins with setting a planning goal and tasks to achieve it.
The purpose of financial planning is to create a system of benchmarks for the most effective financial support of the enterprise.
Tasks of financial planning, as a rule, are determined by the types
and urgency of planning. These include:
- ensuring financial conditions for the development of the enterprise;
- coordination of the amount and timing of cash flows;
- ensuring the timeliness and reliability of the receipt and expenditure of funds of the enterprise;
- ensuring the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise at a given point in time;
- assessment of the effectiveness of decisions made at the enterprise.
Planning subjects- Structural divisions, economic services, specialists, financial managers responsible for the financial planning process at the enterprise.
The subject of financial planning- the process of developing a system of financial indicators that determine the main directions of future activities in the formation and use of enterprise cash funds.
Objects of financial planning:all objects of enterprise financial planning can be grouped as follows:
1. Indicators characterizing the activity of the enterprise.
2. Indicators characterizing financial resources and needs.
3. Cash flows of the enterprise.
4. tax payments.
5. Financial condition and solvency.
1. Indicators characterizing the activity of the enterprise: a) cost results of activities:
Gross turnover;
- commercial products;
- proceeds from the sale of products; b) production costs:
- by elements (raw materials and materials, auxiliary materials, fuel, energy, wages, depreciation, etc.);
- according to costing items;
Direct costing method (direct and indirect);
- in relation to production volumes (constant and variable)
c) income and savings:
Gross income;
- profit and payments from profit;
- funds formed from profits.
2. Indicators characterizing financial resources and needs: a) the amount of own funds; b) the amount of funds raised (borrowed, stable liabilities); c) investment needs;
d) current (financial and operational) needs of the enterprise.
3. Cash flows of the enterprise: a) by type of cash flow:
- cash inflows (inflow of funds to enterprises from various sources);
- cash outflows (expenses of the company's cash in various areas);
- net cash flow of the enterprise (the difference between cash inflows and outflows);
b) by type of activity:
- investment cash flows (inflows and outflows);
- operating (current) cash flows (inflows and outflows);
- financial cash flows (inflows and outflows).
Investment cash flows are the result of investment activities related to the acquisition and sale of non-current assets and other objects of investment activity of the enterprise.
Inflows from investment activities include: proceeds from the sale of fixed assets, intangible assets, the sale of blocks of securities, dividends and interest on acquired securities of other enterprises, proceeds from loans paid by borrowers.
Outflows from investment activities: expenses associated with the acquisition of elements of fixed capital, the acquisition of blocks of securities, the issuance of loans.
Operating (current, basic, production) cash flows are generated from the operating activities of the enterprise, aimed at the production and sale of products or the provision of services.
Inflows from operating activities: receipts from customers for goods sold or services rendered, other receipts not related to investing or financing activities.
Outflows: payments to suppliers for delivered products, payments to employees of various kinds (wages, remunerations, bonuses, financial incentives), tax transfers, provision of commercial loans to buyers, fines, penalties, penalties, others not related to investment and financial activities.
Financial cash flows are formed from financial activities, the essence of which is to attract financial resources to the enterprise. The result of financial activities are changes in the size and composition of equity capital and borrowed funds of the enterprise. Cash flows arising from transactions that cause changes
reflected in the Financial Activities section of the cash flow statement.
Inflows from financial activities: proceeds from the issue of common and preferred shares, proceeds from the issuance of bonds, bank loans.
Outflows: dividend payments on issued shares, buybacks of own shares, repayment of interest on bonds, payments on financial leases, interest to banks and repayment of principal.
4. Tax payments a) in time; b) by type.
5. Financial condition and solvency: a) indicators of financial stability; b) liquidity indicators; c) indicators of solvency;
d) indicators of business activity; e) profitability indicators.
Principles of financial planning. The effectiveness of the organization of financial planning is determined by the observance of the following principles (rules) of planning at the enterprise:
systemic;
continuity;
Flexibility;
- accuracy (completeness);
- consistency;
objectivity;
Clarity.
Systematic planning lies in the need to take into account at the enterprise the entire set of elements of the planning system and the relationships between them.
Continuity of planning means that the planning process must be carried out at the enterprise constantly, taking into account changes and adjustments to the results of past periods.
The principle of flexibility is to give the plans and the planning process the ability to change its direction due to unforeseen circumstances. To implement this principle, plans must be drawn up so that they can be changed, coordinating them with changing internal and external conditions. In practice, this principle is implemented through the formation in the plans of the so-called financial reserve (liquidity reserve, insurance
reserve, reserve fund, etc.), in case of changes and force majeure.
The essence of the principle of accuracy is reduced to concretization and detailing of plans to the extent that the external and internal conditions of the enterprise's activities allow it.
Consistency planning lies in the fact that all indicators of the various plans of the enterprise must be consistent with each other in terms of magnitude and timing of execution.
The principle of objectivity lies in the fact that the plans should reflect real indicators characterizing the current state of the enterprise.
The clarity of planning lies in the development of plan forms that are easy to read and make operational management decisions.
To the main financial planning methodsused in the enterprise include balance, normative, probabilistic, trend extrapolation methods, method of expert assessments, forecasting,economic and mathematicalmethods, the method of optimizing planned decisions, etc. The methods are applied depending on the tasks and urgency of the financial planning of the enterprise.
Essence balance method is manifested in the fact that by building a balance, a link is achieved between the available resources and the actual need (sources of formation). In practice, it is used to calculate the movement of cash flows and funds, payment calendars, income and expenses of the organization. The balance method consists in linking, for example, balances of funds at the beginning of the period, the movement of funds during the period, balances of funds at the end of the period, and reconciliation of the amount of expenditure of funds with their receipt.
Normative method allows the use of pre-developed and established norms and standards for the needs of the enterprise in certain types of resources and sources of their formation, expenditure and deductions of the enterprise. The financial planning system uses various state, municipal, regional, sectoral, internal norms and standards, which include tax and deduction rates, depreciation rates for various groups of equipment, the procedure for distributing profits, working capital standards, the procedure for the formation of production costs, etc. P.
Probabilistic-statistical methods are used to study the dynamics of past periods, analyze structural indicators, identify
deviations and reasons for deviations, obtaining average values (average delivery period, weighted average price of capital), risk assessment, etc.
Trend extrapolation method is based on statistical observation of the dynamics of a certain indicator and determination of its development trend. Based on the observations, the so-called trend line (dynamics) is built and the indicators are extrapolated for the upcoming period of activity. Thus, with the help of this method, the patterns of the past development of the object are transferred to the future.
Method of expert assessments consists in conducting surveys of specialists in the chosen field of knowledge. Such surveys can be carried out, in turn, by the following methods: “interview”, “round table”, “brainstorming”, the method of analytical memorandums, questionnaire survey. The data obtained using the above methods are subjected to statistical processing, as a result of which a range of expert opinions is formed, reflecting their collective opinion on the chosen problem.
Forecasting is a scientific prediction of the course of events, the construction of hypotheses, scenarios, models of economic processes that may take place in the future. Forecasting is usually used at one of the initial stages of the management process in order to assess what management actions can lead to, what are their expected favorable and unfavorable consequences and results. Forecasts are usually built in several versions, which allows you to explore a variety of alternative ways of further action and choose the best of them.
Optimization method consists in drawing up several variants of planned calculations for the selection of the optimal ones. At the same time, the minimum reduced costs, current costs, capital investments with the greatest efficiency of its use, maximization of the reduced profit, cash flow, and return on capital can be used as guidelines.
Content economic and mathematical method lies in the fact that it allows you to find and justify the quantitative expression of the relationship between financial indicators and factors affecting their value. Mathematical models from the total number of factors select those that have the most significant impact on the resulting indicator, based on single or multifactor models (the Altman model for predicting bankruptcy, factor analysis of profitability using the DuPont method, etc.).
The network method allows, based on network diagrams or models, to describe the organizational and technological sequence of execution
operations and interconnections between them, ensure the coordination of operations, coordinate financial resources and sources. A network diagram is an information model that reflects the process of performing a set of operations aimed at achieving a goal or specific tasks. In practice, this method is used in the preparation of a financial support plan for an investment project, a program to bring an enterprise out of a crisis and restore its solvency and liquidity, etc.
Information support of financial planning- this is a process of continuous targeted selection of relevant informative indicators necessary for the implementation of effective management decisions in various areas of the enterprise. These include:
- indicators characterizing the general economic development of the country;
- indicators characterizing the sectoral affiliation of the enterprise;
- indicators characterizing the state of the national and international financial markets;
- indicators formed from the internal sources of information of the enterprise (data of statistical and financial accounting, management accounting, analytical work of the enterprise).
Forms of planning are, as a rule, specific ways of being financial planning for an enterprise. Forms of financial planning are determined by the terms for which plans are drawn up. The forms of financial planning include: balance of income and expenses, enterprise development budget, cash flow budget, sales forecast, cost estimate, etc.
The relationship of types, forms and methods of financial planning can be represented in the form of a table. 5.1.
Table 5.1.
Characteristics of the types, forms and methods of financial planning
Strategic |
Provide |
Long term |
Scenario |
Method of expert |
development |
(more than 1 year) |
development |
estimates, economic |
|
enterprises |
mathematical |
|||
Strategic |
modeling, |
|||
probabilistic - |
||||
Development budget |
statistical |
|||
enterprises |
methods, methods |
|||
extrapolation, |
||||
computer |
||||
modeling, |
||||
forecasting, |
||||
optimization methods |
||||
Provide |
Income balance and |
Balance, |
||
activity |
expenses |
normative |
||
enterprises |
Consolidated budget |
|||
during |
movements |
|||
Money |
||||
enterprises |
||||
Annual budget |
||||
Investment |
||||
predictive |
||||
enterprises |
||||
Promptly |
Provide |
Payment |
Balance |
|
payment method |
calendar, |
Express Methods |
||
obnost in |
cash plans, |
financial |
||
throughout the year |
states |
|||
movements |
||||
Money |
||||
Tax |
||||
calendar |
||||
Shipment plan |
||||
products |
||||
Repayment Schedule |
||||
debt |
The result of financial planningis a set of plans, estimates, budgets, on the basis of which organized, implemented and controlled activities for the financial support of the enterprise.
Financial planning is the basis for financial analysis and control (comparison of plan and fact). In turn, based on the results of financial control and analysis, financial plans are adjusted.
financial planning- this is the planning of all income and directions of spending money to ensure the development of the organization. The main goals of this process are to establish a correspondence between the availability of financial resources of the organization and the need for them, the choice of effective sources for the formation of financial resources and profitable options for their use.
In the process of financial planning, the optimal proportion between financial and material resources is established. Financial planning in organizations is interconnected with the planning of economic activity and is built on the basis of production plan indicators (production volume, sales, production cost estimates, capital investment plan, etc.). In the process of drawing up a draft financial plan, a critical approach is taken to the indicators of the production plan, intra-farm reserves unaccounted for in them and ways to more efficiently use the production capacity of the enterprise, more rational use of material resources, improve product quality, expand the range, etc. are identified and used. planning is designed to determine the optimal proportions in the sphere of financial relations, i.e., to ensure a rational ratio between the volume, growth rates of production and the financial resources of the enterprise, between budgetary, own and credit resources directed to the expansion of production.
Financial planning is carried out by drawing up financial plans of different content and purpose, depending on the tasks and objects of planning. Based on this, financial plans should be divided into long-term, current and operational.
In the long-term financial plan, the key financial parameters for the development of the organization are determined, and strategic changes in the movement of its financial flows are developed. In the current financial plan, all sections of the organization's development plan are linked to financial indicators, the impact of financial flows on production and sales, and the competitiveness of the organization in the current period are determined. An operational financial plan includes short-term tactical actions - drawing up and executing a payment and tax calendar, a cash plan for a month, a decade, a week.
Tasks of financial planning:
identification of reserves for increasing the organization's income and ways to mobilize them;
efficient use of financial resources, determination of the most rational directions for the development of the organization, providing the greatest profit in the planned period;
linking financial resources with indicators of the organization's production plan;
ensuring optimal financial relationships with the budget, banks and other financial structures.
The objects of financial planning are:
Movement of financial resources;
Financial relations arising from the formation, distribution and use
financial resources;
Cost proportions formed as a result of the distribution of financial resources.
Prioritization. Financial planning is connected with the real complexity of the planned objects and processes. In financial planning, it is important to highlight the most significant links and dependencies, combine them into modules that take into account the areas of the financial activity of the organization and are structural elements of a single plan. This approach allows you to break the financial planning process into separate planning calculations and simplify the process of developing and implementing the plan, as well as monitoring its implementation.
Forecasting the state of both external and internal, economic, financial environment of the organization is carried out through a systematic analysis of the main factors. The quality of the forecast also determines the quality of the financial plan.
Ensuring financial security. Financial planning should take into account the financial risks associated with making financial decisions, as well as the possibility of eliminating or reducing risks.
Optimization. In accordance with this principle, financial planning should ensure the choice of acceptable and best alternatives for the use of financial resources in terms of limitations.
Coordination and integration. Financial planning should take into account the integration of various areas of the organization.
ordering. With the help of financial planning, a single procedure for the actions of all employees of the organization is created.
Control. Financial planning allows you to establish an effective system of control over production and economic activities, analysis of the work of all departments of the organization.
Documentation. Financial planning provides a documented representation of the process of financial and economic activities of the organization.
In the practice of financial planning, three methods of planning should be distinguished. In the first method of planning, it is carried out from the bottom up, from the lowest levels of the hierarchy to the highest. The lower structural units themselves draw up a detailed financial plan for their work and are subsequently integrated at the upper levels, eventually forming the financial plan of the organization.
In the second method, financial planning is carried out from top to bottom. In this case, the financial planning process is carried out on the basis of the organization's plan by detailing its indicators from top to bottom in the hierarchy. At the same time, structural divisions must convert the financial plans of higher levels incoming to them into the plans of their divisions.
The third method is counter planning, which is a synthesis of the first and second methods of financial planning. This method involves the development of a financial plan in two stages. At the first stage (from top to bottom), current financial planning is carried out according to the main goals. At the second stage (from bottom to top) the final financial plan is drawn up according to the system of detailed indicators. At the same time, the most successful solutions are included in the final financial plans, upon agreement of various levels.
Essence of financial planning processes
Goals of financial planning:
providing the reproduction process with appropriate financial resources both in terms of volume and structure;
definition of the object of planning;
development of systems of financial plans with the allocation of operational, administrative and strategic plans;
calculation of necessary financial resources;
calculation of the volume and structure of internal and external financing, identification of reserves and determination of the volume of additional financing;
forecast of income and expenses of the enterprise.
Financial planning is closely related and based on the marketing, production and other plans of the enterprise, subject to the mission and overall strategy of the enterprise.
Planning is necessary for:
to understand where, when and for whom the company is going to produce and sell products;
to know what resources and when the company will need to achieve its goals;
to achieve efficient use of attracted resources;
to anticipate adverse situations, analyze possible risks and provide specific measures to reduce them.
Tasks of financial planning
An important task in the field of financial management of an enterprise is the task of budgeting, or the formation of a comprehensive financial plan.
The financial plan provides a clear understanding and the ability to analyze various options for achieving the goals, with the subsequent selection of the optimal ones according to the specified criteria: profit, cash receipts, balance sheet structure, etc. Determines the indicators that will be used in evaluating activities. Discusses possible changes in plans related to the new situation. Corrects plans, taking into account the proposed amendments.
Depending on the tasks set, the following types of budgets are distinguished, which are classified by terms into: short-term (year, quarter); long-term, associated with capital investments (compiled for a longer period).
Stages of financial planning
The main stages of the financial planning process:
Analysis of the financial position of the company.
Drawing up forecast estimates and budgets.
Determination of the company's overall need for financial resources.
Forecasting the structure of funding sources.
Development of an effective control and management system.
Development of a procedure for adjusting the plans drawn up
Methods and types of planning
Planning- this is the development and establishment by the management of the enterprise of a system of quantitative and qualitative indicators of its development, which determine the pace, proportions and trends in the development of this enterprise both in the current period and in the future.
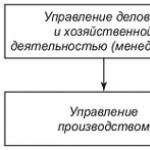
Planning is the central link in the economic mechanism for managing and regulating production. Planning, administrative management and control over the activities of an enterprise in foreign practice are defined by one concept of "management". The relationship between planning and management can be represented as a diagram (Fig. 1).
There are several planning methods: balance sheet, settlement-analytical, economic-mathematical, graph-analytical and program-targeted (Fig. 2). balance method planning ensures the establishment of links between resource requirements and sources of their coverage, as well as between sections of the plan. For example, the balance method links the production program with the production capacity of the enterprise, the labor intensity of the production program - with the number of employees. The enterprise draws up balances of production capacity, working time, material, energy, financial, etc.
Calculation and analytical method is used to calculate the indicators of the plan, analyze their dynamics and factors that provide the required quantitative level. Within the framework of this method, the basic level of the main indicators of the plan and their changes in the planning period are determined due to the quantitative influence of the main factors, indices of changes in planned indicators are calculated compared to the baseline.
Economic and mathematical methods allow you to develop economic models of the dependence of indicators on the basis of identifying changes in their quantitative parameters compared to the main factors, prepare several options for the plan and choose the best one.

Rice. 1. The relationship between planning and managing the production activities of an enterprise

Rice. 2. Planning methods
Graph-analytical method makes it possible to present the results of economic analysis by graphic means. With the help of graphs, a quantitative relationship is revealed between related indicators, for example, between the rate of change in capital productivity, capital-labor ratio and labor productivity. network method is a kind of graphical analysis. With the help of network graphs, parallel execution of work in space and time on complex objects (for example, the reconstruction of a workshop, the development and mastering of new equipment, etc.) is simulated.
Program-target methods allow you to draw up a plan in the form of a program, that is, a set of tasks and activities united by one goal and timed to specific dates. A characteristic feature of the program is its focus on achieving final results. The core of the program is the general goal specified in a number of sub-goals and tasks. The goals are achieved by specific executors who are endowed with the necessary resources. Based on the ranking of goals (general goal - strategic and tactical goals - work programs), a graph of the "tree of goals" type is compiled - the initial base for the formation of a system of indicators for the program and the organizational structure for managing it.
In terms of timing, the following types of planning are distinguished: long-term, current and operational-production (Fig. 3). Forward planning is based on forecasting. With its help, the prospective need for new types of products, the commodity and marketing strategy of the enterprise in various markets, etc. are predicted. Long-term planning is traditionally divided into long-term (10-15 years) and medium-term (3-5 years) planning.
Long term plan has a program-target character. It formulates the economic strategy of the enterprise for a long period, taking into account the expansion of the boundaries of existing sales markets and the development of new ones. The number of indicators in the plan is limited. The goals and objectives of the perspective long-term plan are specified in medium term. The objects of medium-term planning are the organizational structure, production capacities, capital investments, financial requirements, research and development, market share, etc. for 5 years, medium-term - for 2-3 years.

Rice. 3. Types of planning at the enterprise (firm)
Current (annual) planning developed in the context of the medium-term plan and refines its indicators. The structure and indicators of annual planning vary depending on the facility and are divided into factory, workshop and brigade. The main sections and indicators of the annual plan are presented in Table. one.

Table 1 Main sections and indicators of the annual plan
Operational and production planning clarifies the tasks of the current annual plan for shorter periods of time (month, decade, shift, hour) and for individual production units (workshop, site, team, workplace). Such a plan serves as a means of ensuring the rhythmic output of products and the uniform operation of the enterprise and brings the planned targets to the direct executors (workers). Operational production planning is divided into intershop, intrashop and dispatching. The final stage of the factory operational and production planning is shift-daily planning.
In general, long-term, current and operational production planning are interconnected and form a single system. A simplified procedure for developing a comprehensive firm plan includes the following main elements (Fig. 4).

Rice. 4. The procedure for developing a comprehensive plan for an enterprise (firm)
There are various signs of classification of planning by types, terms, forms and other features. From the point of view of the obligation to accept and fulfill plan targets, it is divided into directive and indicative planning. Directive planning is characterized by the obligatory acceptance and fulfillment of plan targets established by a higher organization for enterprises subordinate to it. Directive planning permeated all levels of the socialist central planning system (enterprises, industries, regions, the economy as a whole), and fettered the initiative of enterprises. In a market economy, directive planning is used at the level of enterprises in the development of their current plans.
Indicative planning is a form of state regulation of production through the regulation of prices and tariffs, tax rates, bank interest rates for loans, minimum wages and other indicators. The tasks of the indicative plan are called indicators. Indicators are parameters that characterize the state and directions of development of the economy, developed by government bodies. As part of the indicative plan, there may also be mandatory tasks, but their number is very limited. Therefore, in general, the plan is guiding, recommendatory in nature. In relation to enterprises (organizations), indicative planning is more often used in the development of long-term plans.
It is necessary to distinguish between long-term planning, forecasting, strategic planning, tactical planning and business planning, which are interconnected, form a single system and at the same time perform different functions and can be used independently. As noted above, forward planning is based on forecasting. Forecasting is the basis, the foundation of long-term planning and, unlike it, is based on foresight, built on an economic-mathematical, probabilistic and at the same time scientifically based analysis of the prospects for the development of an enterprise in the foreseeable future.
Strategic planning sets long-term goals and develops the means to achieve them, determines the main directions of development of the enterprise (organization) and, most importantly, forms the mission of the enterprise aimed at realizing its common goal. The mission details the status of the enterprise (organization) and provides directions and benchmarks for setting goals and strategies at various levels of development. Tactical planning, in contrast to long-term and strategic planning, covers the short and medium term and is aimed at implementing the implementation of these plans, which are specified in the comprehensive plans for the socio-economic development of the enterprise.
Mining mining is a kind of technical and economic planning, however, in a market economy, its functions have expanded significantly and it has become an independent type of planning. There are other classifications of forms and types of planning. So, according to the classification of R.L. Akoff, widely used in foreign science and practice, planning can be:
reactive - based on the analysis and extrapolation of past experience from the bottom up;
inactive - focuses on the current situation of the enterprise for the survival and stabilization of the business;
preactive (proactive) - based on forecasts, taking into account future changes and carried out at enterprises from top to bottom by optimizing decisions;
interactive - is to design the future, taking into account the interaction of the past, present and future, aimed at improving the efficiency of the development of the enterprise and the quality of life of people.
It should be noted that planning at an enterprise (firm) is the most important element of the market system, its basis and regulator.
Long-term, current and operational planning
According to the timing, the following types of planning are distinguished: long-term, current and operational-production.
Forward planning is based on forecasting, otherwise it is called strategic planning. With its help, the prospective need for new types of products, the commodity and marketing strategy of the enterprise for various sales markets, etc. are predicted. Long-term planning is traditionally divided into long-term (10-15 years) and medium-term (5 years), or five-year planning.
Rice. 6. Relationship between medium-term and current planning
The long-term plan, for 10-15 years, has a problem-target character. It formulates the economic strategy of the enterprise for a long period, taking into account the expansion of the boundaries of existing sales markets and the development of new ones. The number of indicators in the plan is limited. The goals and objectives of the long-term plan are specified in the medium-term (five-year) plan. The objects of medium-term planning are the organizational structure, production capacities, capital investments, financial requirements, research and development, market share, etc.
Currently, the deadlines for the implementation (development) of plans are not binding and a number of enterprises are developing long-term plans for a period of 5 years, medium-term plans for 2-3 years.
Current (annual) planning is developed in the context of a five-year plan and refines its indicators. The structure and indicators of annual planning vary depending on the object and are divided into factory, shop, brigade.
The relationship between medium-term and current planning is shown in fig. 6.
Operational production planning refines the tasks of the current annual plan for shorter periods of time (month, decade, shift, hour) and for individual production units: shop-site-team-workplace. Such a plan serves as a means of ensuring the rhythmic output of products and the uniform operation of the enterprise and brings the planned target to the direct executors - the workers. Operational production planning is divided into intershop, intrashop and dispatching. The final stage of the factory operational and production planning is shift-daily planning.
In general, long-term, current and operational production planning are interconnected and form a single system.
no comments
Almost all management functions that are found in working socio-economic systems consist of planning.
Financial planning is a system (plan) that allows you to predict financial expenses and ensure the prosperity of the enterprise.
The ability to correctly predict income, take into account cash costs is the basis.
To make a plan, you need to evaluate everything:
- necessary information for planning;
- key elements of the enterprise that will help control funding;
- options to achieve the goal.
Financial planning has a goal - to harmonize and synchronize income and expenses in the enterprise. The plan should be formed according to the production program and development perspective.
Types of financial planning
The financial plan can be of two types: short-term and long-term.
The long-term consists of important proportions, indicators and rates of broad production. As practice shows, it is calculated for several years, even more.
It is necessary to draw up such a plan with the pace of development, it is impossible to be sure of the economic stability of the country. Financial analysts can reliably predict financial opportunities, correctly channel and use them.
When drawing up a long-term plan, it is necessary to develop a financial strategy for the company, which will be able to predict at least 70% of financial activity.
When forming a financial strategy, it is necessary to coordinate everything with your goals and directions, which are spelled out in the overall strategy of the company.
In short-term planning, one should take into account the fact that its relevance is not more than one year (this is the maximum period). You can make up for a month, a quarter, and even a decade (10 days).
Its main goal is to control the profit that goes into the account of the firm in relation to expenditure financing. All your expenses must be financed by profit. This needs to be constantly monitored and shaped in a timely manner, making changes in your financial resources.
To create short-term planning, you must develop a set of short-term planning targets that are related to financing and are aimed at economic activities.
The essence of financial planning
Any enterprise must be able to keep track of finances, otherwise it will not be possible to achieve profit, but only loss. But planning also applies to freelancers, self-employed professionals.
Proper financial planning helps:
- implement the strategic goals that have been developed by specific indicators;
- provide a resource of finance included in the plan for production and economic development;
- determine the capabilities of the enterprise that can be used by competitors;
- to attract investors (entrepreneurs or organizations that have invested in the enterprise);
- will allow you to find and eliminate errors related to finances in time.
Tasks of financial planning
Financial planning has the following tasks:
- Production, investment and financial activities must be fully supported by financial reserves.
- Determine the investment of capital will be effective and evaluate its effectiveness.
- Identify on-farm stocks that can increase profits.
- Establish sound financial relationships with government spending.
- Correspond to the interests of persons included in the joint-stock company and other investors.
The task of financial planning is to control and regulate the financial condition, solvency and creditworthiness.
Quality of financial planning
You need to rely on yourself, it is important to take into account factors when drawing up a plan:
- deadlines for achieving the goals;
- work with investors and competitors;
- long-term perspective.
To plan finances, you need to weigh the risks that will appear in the future.
If there is no experienced financier among the employees, then you need to find him on the side, the performance of the enterprise depends on the management of finances.
Meaning and content
Planning allows you to minimize the uncertainties coming from the market and the negative aspects that can leave a mark on the enterprise.
Thanks to financial planning, they evaluate the economic prospect, the result of financial work.
Calculate the volume of stocks that will lead to the goal. You can calculate how long it will take to return the invested funds to investors.
 Features of financial planning
Features of financial planning Long-term and short-term financial plans evaluate the organization of planned work, control the motivation for the work of personnel.
If you learn how to manage a company and keep a financial report, then it is easy to avoid negative consequences during work.
Entrepreneurs are actively implementing financial planning and note its benefits:
- prepare for and prevent adverse conditions in the company;
- problems can be assessed;
- give incentives to employees to organize work;
- efficient use of resources, strengthen internal control.
Principle of financial planning
The principle of work in the systemic nature of financial planning. What does systemic mean? The system is built from a set of departments of the enterprise and in their relationship. The system is goal oriented.
The principle of coordination of plans - the activities of the branches of the organization must interact with each other. If changes were made to one of the branches, then they must be reflected in the planning of the other.
In finance, there are several essential principles. Let's look at them in more detail.
- Participation . The moment when all specialists working at one enterprise become participants in financial planning. This does not affect the position and role of the activity.
- Continuity. Each company has its own cycle, and planning occurs within cycles. This is a systematic principle, all the ideas of the cycle must be transferred to others. If during this period there are financial costs and changes within the company, then it is necessary to adjust the financial plan and clarify the details.
- Flexibility. The principle has a fine line with continuity. This moment gives the opportunity to change plans due to circumstances. This will solve the problems of the company without problems and losses. The specialist must anticipate possible circumstances, create a “safe reserve”.
- Accuracy . Each plan must be specific and detailed so that external and internal provocations do not affect the work of the organization.
- Financing term. This principle is the foundation of banking. It is necessary to receive profit and spend all funds strictly according to the terms established in the plan. If you need to invest money for a long time (the period until they pay off), then you need to do it with a long-term loan.
- Solvency. You must plan your cash so that the firm is solvent, no matter what the situation. You must have funds that can be quickly turned into money). This will help you to pay off the required payments in a short time.
- Return on equity. Capital investment should act as the cheapest way of financing.
- Balanced risks. If you have taken a long-term investment, which is risky, then you need to finance it with your own money, this will be net profit and depreciation.
- Adaptation to the market. It is necessary to take into account the needs of the market, to calculate how much you depend on the loans that you have been provided.
- marginal profitability. Properly use those investments that are most cost-effective
Financial planning has a fine line with marketing.
Remember that until you develop a marketing and production strategy, you will not be able to predict your financial affairs and the financial forecast will lose its value.
For the convenience of studying the material, we divide the article into topics:
The objectives of financial planning are:
Ensuring the trading process is necessary;
- establishment with the budget, banks and other contractors;
- identification of the directions of the most profitable financial investments;
- increasing the profitability of financial and economic activities;
- control over the formation and expenditure of funds.
The financial plan is an integral part of the business plan of the enterprise. When developing a business plan, it is planned to proceed from the fact that the determination of the funds necessary to finance the development of an enterprise involves evaluating this plan as an investment project. This means that the enterprises envisaged by the plan must be justified by them.
There are two types of financial planning in a business plan: strategic and tactical.
A strategic (prospective) financial plan is a form of implementing the goals and objectives of an enterprise, an investment strategy and expected savings. The basis of strategic financial planning, which is one of the commercial secrets of the enterprise, is the determination of the capital requirement for entrepreneurial activities. A tactical financial plan is an annual balance of income and expenses of an enterprise. In the context of inflation, financial plans are drawn up for the quarter and adjusted to the inflation index.
The purpose of drawing up a financial plan is to link the income of the enterprise with the necessary expenses. When income exceeds expenses, the excess amount is sent to the reserve fund; when expenses exceed income, the amount of lack of financial resources is determined.
An enterprise can raise additional funds by issuing securities, obtaining credits or loans, sponsorship contributions, etc.
In the financial plan, a specific link is made between each type of investment or fund and the source of their financing. For this, a check (chess table) is compiled, in the vertical columns of which the directions for the use of financial resources are given, and in the horizontal columns - sources of financing, which corresponds to the expenditure and revenue parts of the balance sheet. The chess table allows you to identify the targeted nature of the use of resources and balance income and expenses by item.
The main income items of the financial plan are profit, bank loans and other income and receipts; the main items of expenditure are tax deductions, expenditures on capital investments, funds for the repayment of bank loans and interest on them and growth, deductions to trust funds and other expenses and deductions.
In practice, financial plans concretize strategic ones. In turn, tactical plans are detailed through operational planning, which is the development of operational financial plans: cash plan, credit plan, payment calendar, etc.
The cash plan reflects the cash flow of the enterprise during a certain period (most often a quarter). It is poor cash management that is the main cause of financial and economic difficulties, therefore the preparation of cash plans and control over their implementation are important for increasing the solvency of an enterprise.
Credit plan - a plan for the receipt of borrowed funds and a debt repayment schedule. Usually issued in the form of a credit rate.
Payment calendars, the time horizon of which ranges from 5 to 30 days, reflect operational data on the movement and balances of funds for enterprises.
Ultimately, financial planning is aimed at ensuring the rational and efficient use of the financial resources available to the enterprise.
Financial planning at the enterprise
Let us dwell on the financial, which plays a paramount role. The management of the enterprise must know what tasks in the field of economic activity it can plan for the next period. Those interested in the activities of the company impose certain requirements on the results of its work. When planning certain types of activities, it is necessary to know what economic resources are required to complete the tasks. This applies, for example, to planning in the field of raising capital (purchasing loans, increasing, etc.) and determining the volume of investments.As the budgeted plans are implemented, it is necessary to record the actual results of the firm's activities. Comparing the actual figures with the planned ones, it is possible to carry out the so-called budgetary control. In this sense, the main attention is paid to indicators that deviate from the planned ones, and the reasons for these deviations are analyzed. Thus, information about all aspects of the company's activities is replenished. Budget control allows, for example, to find out that in some areas of the company's activities, the planned plans are being implemented unsatisfactorily. It is possible, of course, to assume a situation where it turns out that the budget itself was drawn up on the basis of unrealistic assumptions. In both cases, the management is interested in getting information about it in order to take the necessary actions, i.e. change the way plans are carried out or revise the provisions on which the budget is based.
The budget is an action program (plan) expressed in terms of cost in the field of production, procurement of raw materials or goods, sales of manufactured products, etc.
The action program should provide for temporal and functional coordination (coordination) of individual activities. sales depends, for example, on the value of the expected price of the supplier and the conditions of production; the number of products produced - from the expected volume of sales; the value of the selling price - on what volumes of purchases of raw materials and materials are required by the production and sales program, etc.
When developing a budget for the next period, a decision should be made in advance, before the start of activities in this period. In this case, there is a greater likelihood that the planners will have enough time to put forward and analyze alternative proposals than in the situation where the decision is made at the very last moment. In other words, in the last example, the firm is at great risk of taking the path of least resistance.
The approval by the management of the firm of the budget (plan) of the unit serves as a signal that in the future operational decisions are made at the level of this unit (decentralized), if they do not go beyond the budget limits. If budgets at the level of divisions are not developed, the company's management is unlikely to be inclined to decentralize the process of making operational decisions.
The organization of work on intra-company planning depends on the size of the enterprise. In small firms, there is no separation of management functions in the true sense of the word, and managers have the opportunity to delve into all the problems on their own. In large enterprises, budgeting work should be decentralized. After all, it is at the level of departments that the personnel with the greatest experience in the field of production, procurement, sales, operational management, etc. are concentrated. Therefore, it is in the subdivisions that proposals are put forward regarding the actions that it would be advisable to take in the future.
Departmental budgets are not developed in isolation from each other. When calculating, for example, planned sales figures, and hence the amount of coverage, it is necessary to know the production conditions and planned selling prices. In order to ensure an effective coordination system, many enterprises develop an instruction for budgeting, which contains a time plan, as well as the distribution of duties and responsibilities when calculating budget indicators.
Usually, there are two schemes for organizing work on budgeting (plans): according to the top-down method and according to the bottom-up method. According to the first method, the budgeting work starts "from the top", i.e. the company's management determines the goals and objectives, in particular the targets for profit. Then these indicators in more and more detailed form as you move to lower levels of the enterprise structure are included in the plans of departments. The second method does the opposite. For example, the calculation of sales indicators is started by separate sales departments, and only then the head of the sales department of the company brings these indicators into a single budget, which can later be included as an integral part of the overall budget of the enterprise. In practice, it is impractical to use only one of these methods. Planning and budgeting is an ongoing process in which it is necessary to constantly coordinate the budgets of various departments.
The firm must plan and control in two main economic areas. We are talking about the profitability (profitability) of its work and financial position. Therefore, the profit budget and the financial plan are the central elements of intra-company planning.
The natural basis for the formation of the profit budget for the future period is the profit report. The income statement reflects the economic results of operations in the past period. This kind of information is, of course, of great importance in forecasting the economic results of actions planned for the future period.
Even if the same actions are planned for the coming year as were carried out in the reporting year, the amount of income in the next year will differ from the amount of income reflected in the report for the last year. The fact is that all the time there are changes in the external conditions of the company.
Macroeconomic factors may, for example, change under the influence of inflation, changes in foreign exchange relations and income policy. It can be assumed that it will amend the economic legislation. The structure of demand in individual market segments may change due to changes in the structure of the population.
The special importance of the quality of financial planning in enterprises is increasing. The financial plan of the enterprise is interconnected with other aspects of planning the economic activity of the enterprise. These include plans for the sale of products, raw materials, production, advertising, investment, research and development, attraction and return of borrowed funds (credits and from other sources), distribution of income, as well as cost estimates.
The direct basis of the financial plan is the forecast calculations for the sale of products to consumers or plans for its sale, based on orders, forecasts of demand for products and goods, levels of selling prices for them and other market factors. On the basis of sales indicators, production volumes, costs of manufacturing products, carrying out work and providing services, as well as profits and other indicators are calculated.
The purpose of the financial plan of the enterprise, on the one hand, is the forecast of the medium-term financial outlook, and on the other hand, the determination of the current income and expenses of the enterprise. The financial plan is compiled by the enterprise for a year with distribution by quarters, as well as for 3-5 years - by years. It reflects income and expenses by items and proportions in the distribution of funds.
It should be noted that within the framework of the annual and quarterly financial plans, there is no influence of intra-month deviations from plans in the activities of the enterprise that affect the financial condition of enterprises during the month, which more often happens during the first 15-20 days of the month, when enterprises usually experience failures in connection with the shortfall in relation to the contractual terms of material and technical resources.
Financial planning at enterprises largely depends on the quality of forecasts of the main indicators of their production activities, market conditions, the state of money circulation and the ruble exchange rate. Therefore, under the current conditions, an underestimation of the need for financial resources and changes in the financial condition of enterprises is possible, and therefore it is necessary to provide for financial reserves.
The composition of indicators of the financial planned balance or balance of income and expenses is determined by the sources of receipt of funds, on the one hand, and the costs and expenses incurred in the course of financial and economic activities, on the other hand. Along with this, the planned balance of income and expenses reflects financial relations with the banking and insurance systems and transactions for the acquisition and issue of securities.
In addition to the balance of income and expenses, the financial plan contains calculations of a number of fundamental indicators:
Profits from industrial activities;
- depreciation deductions for restoration;
- receipts of funds in the order of long-term and medium-term lending;
- interest to banks on loans, financial results from other activities, etc.
The composition of the indicators of the planned balance of income and expenses of the enterprise is a certain system that allows, within each planning period, to determine:
Sources of costs (expenses), their ratio;
- degree and directions of use, distribution of sources;
- balancing them with costs or expenses.
Thus, the remaining part of the profit after paying taxes is used for the needs of the enterprise, including:
Creation of a financial reserve;
- financing and growth of working capital;
- payment of interest to banks for the credit resources provided by them;
- payments to owners of securities issued and sold by the enterprise to its employees;
- expenses for the economic maintenance of socio-cultural and social facilities, for other purposes.
Financing of capital investment costs is carried out at the expense of depreciation deductions for the full restoration of fixed assets, involvement in the investment process of excess stocks of equipment, machinery and materials, profit directed to, as well as by attracting equity capital, funds from the placement of targeted loans and from other sources etc.
Financial planning methods
The quality of financial plans largely depends on the planning methods used.Planning method - methods and techniques for calculating indicators.
In terms of financial planning, there are six methods for justifying planned values.
The "dual" content of financial planning (planning of assets and liabilities and receipts and payments) reflects the fact that there are two objects of financing: assets and operations.
The sources of financing assets are liabilities, i.e. obligations. arising from the enterprise as a subject to the owners of the resources used by the enterprise in its activities, These obligations may be debt [i.e. borrowed], subject to return upon the expiration of their provision, and equity [unlimited], forming the obligations of the enterprise to its legal owners [shareholders. participants]).
Sources of financing operations are liquid assets that can be used as means of payment (normal sources of financing operations are cash and commercial assets).
Financial stability
In the fourth section, the calendar of wages for workers and employees is filled out, which indicates the amount of cash payments to the enterprise on time (a specific day of each month). These amounts, in accordance with the contract of settlement and cash services, the bank issues to the enterprise for the fee established in the contract.
The calculation of the need for a short-term loan is carried out if the company experiences such a need. In this case, the necessary documents are submitted to the bank and a loan service agreement is concluded with it. However, this should be preceded by a reasonable calculation of the amount of the loan, as well as the amount that, taking into account interest, must be returned to the bank.
Current financial planning
The current planning of the financial activity of the organization is based on the developed financial strategy and financial policy for certain aspects of financial activity. This type of financial planning consists in the development of specific types of current financial plans (budgets), which enable the organization to determine for the coming period all sources of financing for its development, form the structure of income and costs, ensure constant solvency, and also determine the structure of assets and capital at the end of the planned period.The current financial plan is drawn up for a period of one year, broken down by quarters, since such a period of time complies with the legal requirements for the reporting period. The current planning is considered as an integral part of the long-term plan and is a specification of its indicators. Recently, organizations are increasingly using the system of activities of structural divisions and the organization as a whole, which is being implemented in order to strictly save financial resources, reduce unproductive costs, greater flexibility in management and control over, as well as to improve the accuracy of planned indicators, comply with the requirements of laws and contracts .
The main advantages of implementing the principles of budget planning are:
Rational use of the organization's funds due to timely planning of business transactions, financial and material flows;
more accurate indicators of costs and profits than in long-term financial planning;
great material interest of workers in the successful fulfillment of planned targets;
implementation of the regime of austerity of financial resources of the organization, etc.
Budgeting is based on certain principles:
The principle of harmonizing goals;
the principle of responsibility for their formation and execution;
the principle of flexibility.
A budget is a coordinated financial document that reflects the receipts and expenditures for a particular line of business. The budgeting process is a technology of financial planning, accounting, analysis and control of the activities of the enterprise as a whole and its individual structural divisions, which is based on the development of budgets according to certain rules.
Budgeting is necessary for planning financial and economic activities, coordinating the activities of various departments of the enterprise, stimulating managers at all levels in achieving relevant goals, monitoring current activities, evaluating the implementation of the plan by various departments (responsibility centers).
Budgeting technology includes the formation and consolidation of enterprise budgets. For this, the financial structure of the enterprise is being developed, which is a set of departments (responsibility centers). For each of them, the corresponding budgets are formed separately - operating, investment, financial. Operating budgets include:
1. sales budget;
2. production budget;
3. inventory budget;
4. the budget of direct labor costs;
5. budget of direct material costs;
6. production budget;
7. budget;
8. budget for management expenses.
Investment budgets include: a) real investment budget; b) financial investment budget.
The financial budget consists of: a) the cash flow budget; b) income and expenditure budget; c) balance sheet.
In turn, the main (consolidated) budget is a consolidated financial plan, which is developed on the basis of budgets of various types or structural divisions of the enterprise. The main budget acts as a link between the various plans of the organization and is expressed in the formation of financial budgets that bring together all its other plans (budgets) in a cost estimate.
The development of budget planning technology in an organization is carried out in the following sequence:
2. Absorption costing - a method of accounting for full costs, in which all direct and indirect - general production costs are included in direct production costs when calculating profits and income tax.
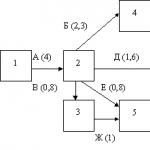
In the practice of tax calculations in the country, the second method is adopted. To illustrate, consider an example with the following data: 15 items were manufactured and 10 items were sold. at a price equal to 20 thousand rubles; the cost of materials and wages of production workers are equal to 5000 rubles. for one product; overhead costs in the sales period are 60 thousand rubles. administrative expenses amounted to 50 thousand rubles. So, according to the direct costing method, the profit is equal to
20,000 X 10 - 5,000 X 10 - 60,000 - 50,000 = 40,000 rubles; according to the absorption costing method, the profit is equal to
20,000 x 10 - (5,000 + 60,000/15) x 10 - 50,000 = 60,000 rubles.
Back | |