Leakage of the heating system is not uncommon, and in most cases it happens unexpectedly, except for test runs at the beginning of the heating season. What caused the leak is not always possible to determine reliably, and it is not always important, since in the foreground in such situations is the restoration of the tightness of the heating circuit. As a rule, a thorough repair is postponed for the warm season, and if a leak is detected, they choose how to cover up the leak in the heating pipe temporarily.
The heating system consists of the following main elements:
- heating boiler;
- pipeline;
- radiators;
- control and measuring and shut-off valves.
All of the listed elements are mounted in a heating circuit, the tightness of which depends on the integrity of the elements and their connections.
The choice of method for restoring the integrity of the heating system depends on the following factors:
- accessibility of the damage site;
- leakage status (fistula, loss of tightness of a threaded connection, etc.);
- the material of manufacture of the damaged element;
- the possibility of shutting down the system.
Based on the combination of the above circumstances, a method is chosen how to most effectively close the leak in the heating pipe in the current situation.
Preparatory work
When spot repairing the heating system, first of all, it is necessary to establish a specific place for the leakage of the coolant. If the pipeline is laid hidden (in the wall, in the floor), lined with decorative elements or equipped with thermal insulation, the task becomes more complicated.
Important! In a situation where a pipe or a joint embedded in a wall has leaked, it is advisable to consider the possibility of installing a new section of the pipeline, since it does not make sense to spoil the finish of the room for repairing a pipe with a high degree of wear.
On the alleged emergency section of the circuit, decorative trim and thermal insulation are dismantled, the place of leakage is found, after which the nature and extent of damage, as well as its availability for repair, are assessed.
Spot repair of the heating system can be of three types:
- mechanical - with the use of compressing and tightening devices, electric welding and other means that are not based on the use of sealing solutions;
- chemical - using various kinds of sealing compounds that harden as a result of chemical reactions or drying;
- combined - sealing the circuit using a combination of mechanical and chemical methods.
If a mechanical method of repair is chosen, and the damage is not significant (needle fistula or drip leak), the heating system can be left in operation before starting work to eliminate the leak. If the damage is more serious, then the heating must be turned off:
- the autonomous boiler is turned off, the coolant is drained;
- in the central heating system, it is necessary to close the valve of the common riser and hang a warning sign on it, after which the water must also be drained from the system.

The technology of processing the base before sealing the contour depends on the material of the pipeline, the status of the leak and the type of repair, but, in any case, the final result of the work is largely due to the quality of the surface preparation.
Methods for performing repairs with reference to the place of leakage
In most cases, it is possible to eliminate the leakage of the heating system on your own, without the involvement of professionals. To do this, consider the methods for producing spot repair of the contour for the most common damage.
Elimination of a fistula in a straight section of a steel pipeline by mechanical means
On a horizontal or vertical section of a solid steel pipe, due to a number of factors (wear, corrosion, material defect), a leak often occurs that can be eliminated independently and without significant costs.
If a fistula with a jet cross section of approximately a match has formed in a steel pipe with a diameter of up to 50 mm, then it can be eliminated even without special preparation of the base, but the thickness of the pipeline wall must be at least 3 mm. The area around the damage is cleaned of rust and scale with a file or grinder, after which a self-drilling screw with a sealing rubber washer is screwed into the hole with a drill. The length of the screw is selected in such a way that it protrudes minimally at the exit from the hole inside the pipe and in no case rests against the opposite wall.

Important! When using an electric drill, the coolant in the pipe must not be under pressure so that the water jet does not hit the tool and cause an electrical injury or breakage of the drill. For safety reasons, it is better to use a drill with a built-in 12 V battery, wrapped in a plastic bag with a slot for a chuck.
It is also better to know in advance how to close a hole in a heating pipe with a diameter of 50 mm or more and with a larger fistula cross section, since the consequences of damage to such a heat pipe are more serious, and the probability of an accident is no less.
The hole of the fistula is driven with a drill of a slightly larger diameter in such a way that then a bolt thread can be cut in it. The wall thickness must also be sufficient for threading. The table shows the correspondence of drills and threads (tap).
Standard Pitch Metric Hole Diameters
After cutting the thread, a bolt with a washer and a rubber seal is screwed into the hole. The length of the bolt is selected depending on the wall thickness - the part after screwing should not block the pipe lumen or rest against the opposite wall.
It is possible to eliminate the leakage of a steel heating pipe without threaded elements - by caulking and electric welding. The hole is drilled to the nearest diameter, after which a cone (chop) of a suitable size, machined from steel, is hammered into it with a hammer. The part of the chop remaining outside is ground down by a grinder to such an extent that a small protruding hat remains, which is then scalded by electric welding. This method of eliminating leakage is reliable and durable, but it should be remembered that rutile-coated electrodes must be used for welding galvanized pipes, and the pipe wall thickness must be sufficient (3 mm).

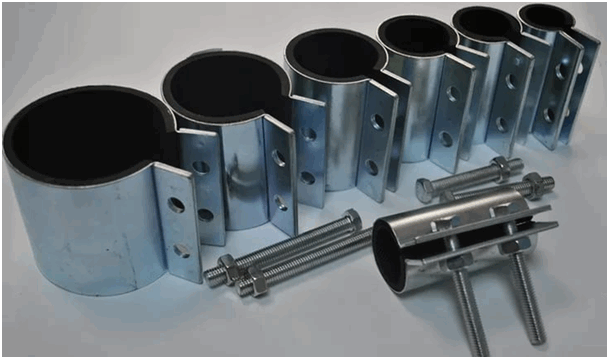
A single hole in the wall of a steel pipe can also be plugged with a narrow clamp.

Such a clamp can also be made independently from strip steel, but there is a large assortment of these devices on sale, the aesthetics of which are much higher. The clamp is selected according to the diameter of the pipe and, if there is no sealing rubber included with it, a gasket made of rubber or paronite with a thickness of at least 3 mm is cut out to it. The device is put on the pipe, the gasket is combined with the fistula, and the clamp is crimped with the necessary force. This method of eliminating leakage is also applicable to pipelines made of copper or polymeric materials.

In a situation where several fistulas have formed on a small area, it is impossible to use the above repair methods - the pipe section is weakened, and it is not effective to repair leaks individually and even fraught with the destruction of the entire contour fragment. For damage to an oblong shape (crack), a narrow collar, like a chop, cannot be installed.
If at the moment it is not possible to replace the entire emergency section, then clips are used to restore the tightness of the heating pipeline - wide clamps, the principle of operation of which is the same as that of narrow devices.
Repair of a pipeline in a straight section or a turn by chemical and combined methods
To eliminate the leakage of the heating pipeline, various types of heat-resistant one- and two-component sealants are produced, used on both steel and polymer pipes. The most widespread are high-temperature silicone-based compounds, characterized by a high degree of adhesion, plasticity and the ability to withstand temperatures up to 350 degrees. These sealant mixtures differ from other types of silicone adhesives by having a reddish or brown tint.

Each of these compositions has its own instructions for use, set out on the packaging and providing for the use of joints and mates for sealing. But, if reinforcement is applied, they can also be used on a plane, that is, on the surface of a pipeline, both steel and polymer.
Before starting work, the coolant is drained from the heating system, and the area around the damage is cleaned of paint, degreased and dried.
Important! The adhesion of silicone sealants to smooth surfaces is stronger than to rough ones, therefore, the repaired section of the pipe should not be treated with abrasives.
Reinforcement of the silicone sealing coating is made to increase the tensile strength of the shell and its resistance to mechanical damage. Serpyanka is used as reinforcement - fiberglass masking tape.

A sealant is applied to the prepared surface of the heating pipe in a continuous layer 2-3 mm thick, on top of which a sickle is screwed - in butt turns. A layer of sealant is again applied over the first layer of the mesh, and then a sickle again, but with 5 mm overlapping turns on each other. In total, there should be 4 or 5 layers of mesh with layers of silicone. It is necessary that the turns fit into an interference fit, without folds with voids, like bandaging - with the tape turning around the axis at the end of each layer to return in the opposite direction. Such bandaging should capture sections of the pipeline 10-20 cm in both directions from the damage. The last layer on the pipe is made of sealant, which is smoothed out with a hand dipped in soapy water. The end of the sickle is temporarily attached to the pipe with a nylon clamp away from the repaired area - after the composition has cured, it is cut off flush with the surface of the sealant.
Depending on the type of adhesive and the total thickness of the sealing layer, curing, which occurs from the contact of the composition with atmospheric moisture, requires from several hours to a day.
Using the same technology, using sickle reinforcement, they repair the heating system using heat-resistant rubber sealants - also durable, but elastic compounds that are successfully used both in everyday life and in production.
Keep in mind that silicone and rubber sealants are commercially available for use in automotive engines. If the performance characteristics of such compositions meet the requirements of the heating system, then the auto-sealant, designed for use in the repair of an internal combustion engine, will cope even more with the sealing of the heat pipe in everyday life.

To fix a leaking pipe in a domestic heating system, ready-made repair kits are often used, which include everything necessary for sealing. An example of such tools is the Siloplast repair kit, even equipped with protective rubber gloves. The main element of the leak elimination in the kit is a tape with special impregnation, which, upon contact with water (wetting during installation), hardens and forms a strong hermetic shell on the pipe, which does not need to be additionally coated with anything.

The method of application of Siloplast is described in detail on the packaging, and the success of the repair depends on the observance of this technology, as well as the quality of the base preparation. The repair kit can be used not only on straight, but also on curved sections of the pipe, as well as over threaded connections, the sealing material of which has lost its properties.
The material is produced for various areas of production, so when buying, you need to choose exactly the type of repair kit you need, one of them is Siloplast "For Home".

To restore the tightness of the heating system, special two-component compositions called “cold welding” are also used - mixtures based on epoxy resins with the addition of metal filler and additives that are responsible for the specific characteristics of the adhesive under certain conditions.

The resin in the composition ensures the plasticity of the material after curing, and the metal-containing component increases the strength and hardness of the binder. Cold welding is produced in liquid and plastic form. Specifications, including operating temperature and method of application, are indicated on the packaging. It remains only to choose the right type of sealant that corresponds to the operating conditions and the material of manufacture of the thermal circuit.

If the heating pipe does not leak significantly, then the question of how to cover the contour in a straight section or a joint of a threaded connection can also be solved with improvised means, for example, using Minutka glue or identical in action. To do this, the repaired surface or crack must be cleaned of paint, degreased and dried. Then the prepared area is wrapped with a layer of sickle butt and ordinary baking soda is rubbed into the cells of the grid (preliminarily, the first turn is pointwise attached to the pipe with glue). Then another layer of mesh turns, already overlapped, is applied to the pipe, and the cells are again filled with soda. After laying the third layer of sickle with soda, the last turn of the tape is fixed with a nylon clamp, and glue from a tube is applied to the resulting clutch, starting from the site of damage. The glue is instantly absorbed into the soda and, reacting with it, also instantly hardens, forming a strong shell. It is necessary to apply glue to the entire surface of the winding, the tubes are squeezed out one by one as they are emptied, the number of tubes depends on the area of the repaired area.
If the damage to the pipe is a crack, then it is also stuffed with soda and glue is dripped on top, instantly sealing the damage. A sickle bandage is applied over the crack in the manner described above.
The method is applicable for the repair of both steel and polymer pipes.
There is another way to seal coolant leaks on a straight or oval section of a steel heating pipeline, as well as on top of a threaded connection - using a reinforced cement mortar bandage. To do this, the system is depressurized so that water does not ooze from the damage site, and the repaired area is cleaned of paint and rust. Then, an aqueous solution of the consistency of sour cream is prepared from cement grade 400 or 500, and the problematic section of the pipeline is bandaged in layers with a strip of canvas fabric that passes liquid well through itself (you can use a sickle or an ordinary medical bandage). Bandaging is carried out with coating of each layer with cement mortar. As a result, a sleeve with a wall thickness of at least 2 cm should form on the pipe, which is covered with the last layer of the same solution.

The effectiveness of the method can be increased if, for mixing cement, not water is used, but PVA glue, but not its pasty variety, but emulsion. In addition, cement-based coating waterproofing can be used instead of cement.
Ceresit CR 65, designed specifically for the installation of waterproof coatings.
Important! The use of a cement bandage for sealing the heating pipeline is a temporary measure, since the cement is not plastic and poorly resists the tensile forces that will affect it during the thermal expansion of the pipes, so even reinforcement with sickle will not save from the occurrence of microcracks in the repair shell over time.
Elimination of leakage in places of threaded connections
If the coolant flows at the junction of pipe sections made by the threaded method, or at the points of connection to the heating radiator, shutoff valves, then the best action would be to dismantle the threaded connection to diagnose the cause of depressurization. This refers to the situation when, during the installation of the heating system, fittings designed for adjustment - adjustment with a seal were not used. The dismantling of the threaded connection, which is carried out after the coolant is drained from the system, will show the cause of the leak - thread wear or loss of sealant qualities.
In the first case, the thread profile is refreshed by passing a lerki (die) along it with cutting an additional 2-3 turns. If the thread is significantly destroyed, then you will have to insert a new pipeline fragment by welding or, again, a threaded connection (drive).
If the thread is in satisfactory condition, the sealing material is replaced. To do this, the threads are cleaned of the remnants of the old sealant and a new one is applied to it. For reliable sealing, it is recommended to use a combination of a fiber sealant (linen strand) and one of the types of sealant for threaded joints, including anaerobic ones, designed for independent use.

You can simplify this procedure by using a special universal impregnated sealing thread. The material of the thread can be natural or synthetic, impregnation is most often silicone. Such a thread is attractive by its ease of use, versatility and affordability, which allows you to carry out repairs yourself and without significant costs.

FUM-tape is widely used as a sealant for a threaded joint - a synthetic material that, due to its fluorine content, is resistant to high temperatures and chemicals.
FUM tape is produced in three types:
- FUM-1 - with vaseline-based lubricant, for use in industrial pipelines, including those with aggressive media;
- FUM-2 - does not contain lubricant, suitable for environments with oxidizing agents;
- FUM-3 - for pipelines with non-aggressive media.
All three types of FUM tape are suitable for use in domestic heating systems and are quite effective when properly applied to the thread.

In cases where the leakage intensity is not significant, the dismantling of the threaded connection can be postponed until the end of the heating season, and the tightness of the connection can be restored by applying a reinforced bandage over the joint using one of the sealing compounds described above - silicone, rubber, cold welding.
Conclusion
When fixing a leak in a heating system, the effectiveness and longevity potential of the repair should be objectively assessed. Most of the remedies offered by manufacturers to eliminate leakage are designed to temporarily eliminate an emergency before radical measures are taken, including a major overhaul of the heating system. Therefore, after diagnosing the causes of the leak and choosing how to cover up the damage, it is necessary to consult with professionals, not relying only on marketing advice in the store, sometimes provided by workers without experience in repair and construction activities. This will make it possible to obtain an objective assessment of the situation and correctly plan repair activities at the end of the heating season in order to avoid aggravating the situation in the cold season.





